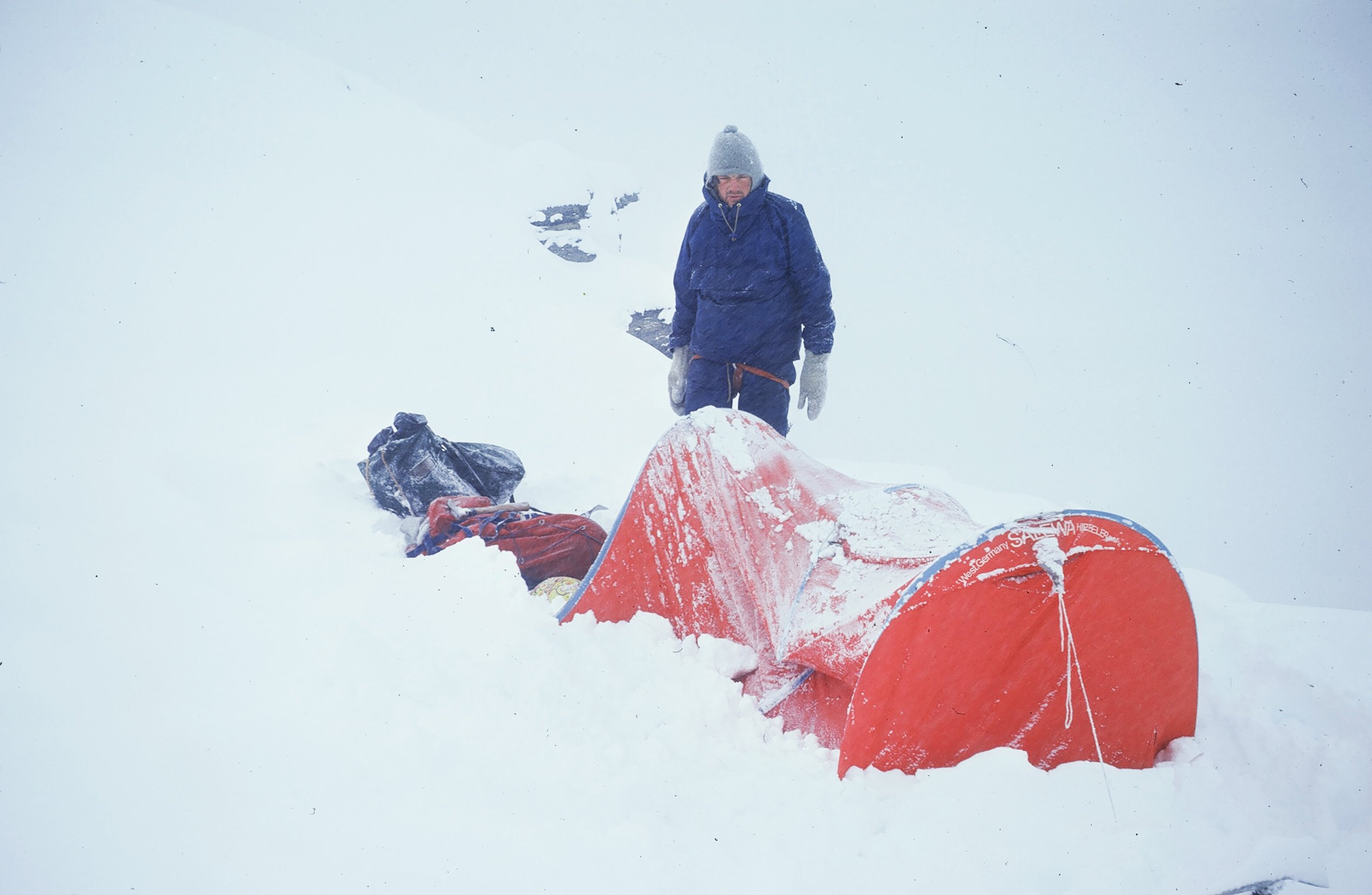
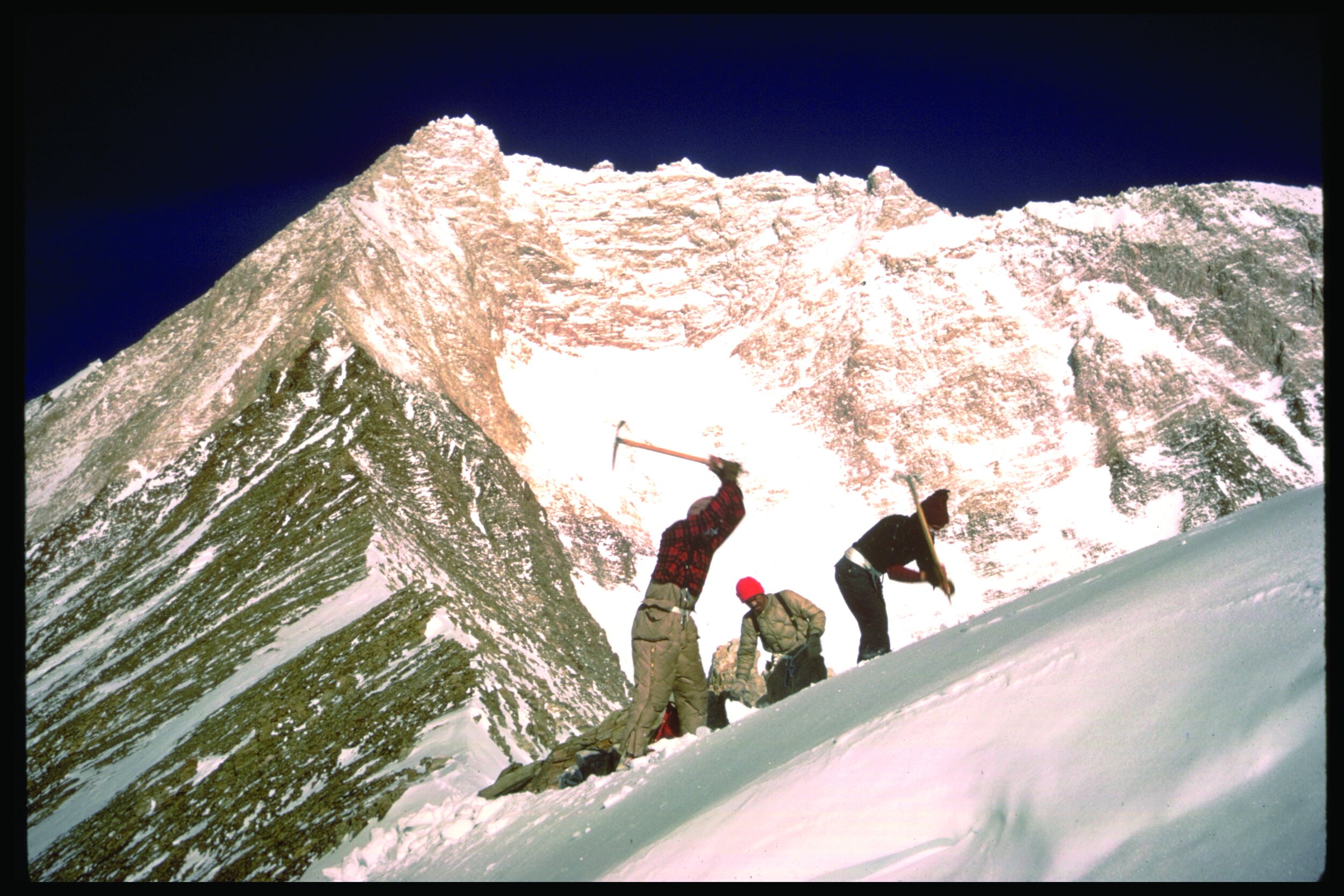
Powered by the AAC’s Catalyst grant, Jessica Anaruk and Micah Tedeschi took on to the big walls of the Mendenhall Towers, seven granite towers that rise high above the surrounding Mendenhall Glacier in southeast Alaska.
Found in Translation
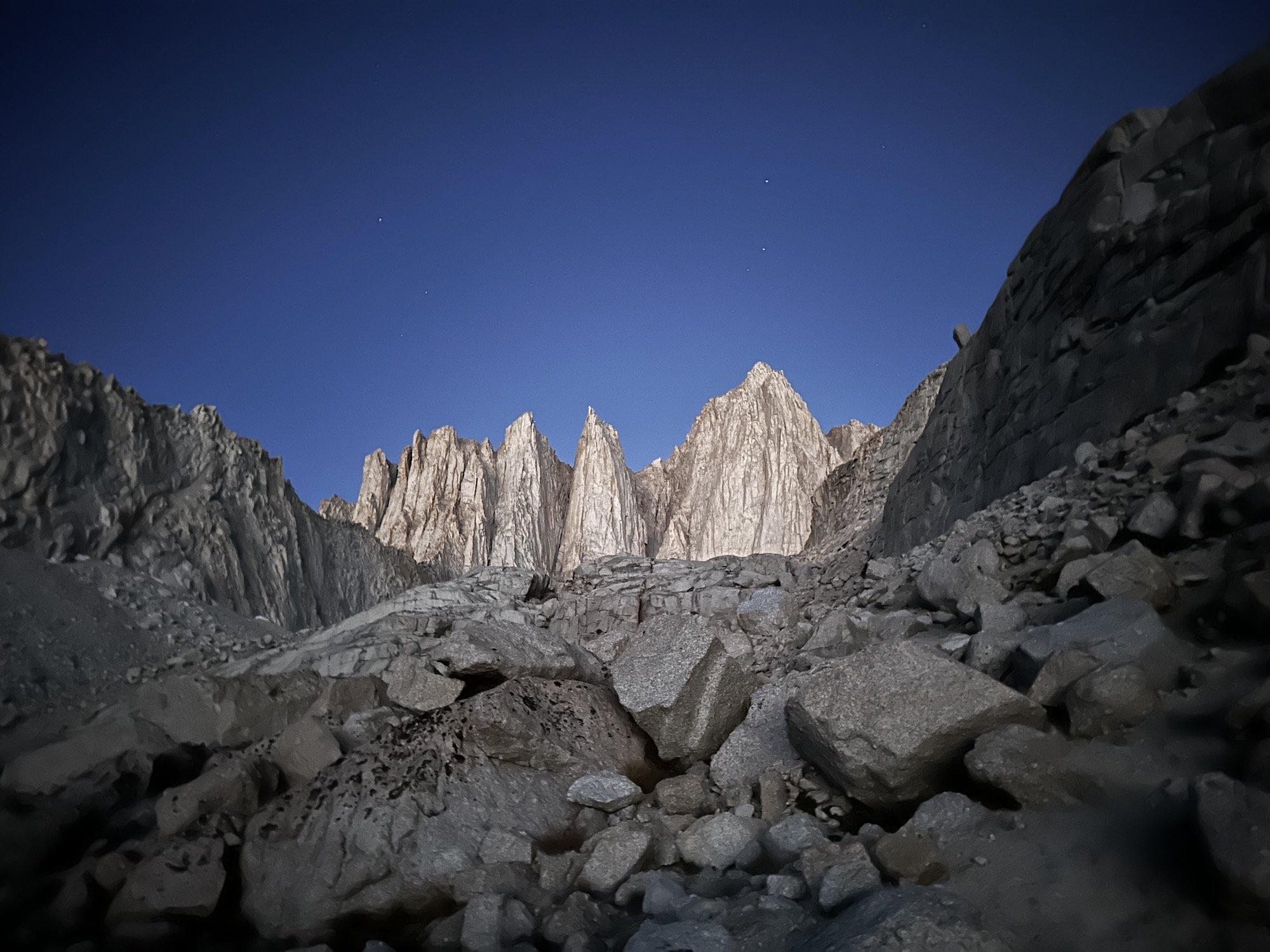
CONNECT: Remembering Charlie Through an Epic on Mt. Whitney
In this episode, we’re sitting down with AAC member David Corvi to talk about his Live Your Dream grant experience—a beautiful day that turned into a 24 hour epic on Mt. Whitney in September of 2024. Getting off route, climbing through pockets of ice and show, and getting lost on the descent were only some of what the team experienced that day.
Because there is another layer of complexity to this story, a mental load that added a unique weight to that experience. David’s trip to Whitney was also in memory of his stillborn son, Charlie. In the episode, David shares about his family’s experience with infant and child loss, how climbing and other forms of outdoor adventures have helped him process his grief and continue to parent Charlie even though he is gone, and likewise he reflects on how physical challenges, like half marathons and the Whitney trip, are a way to honor the life Charlie won’t ever get to experience. Dive into this episode to hear about your classic alpine day gone wrong, and just one way that grief and loss can be processed in the mountains.
David and his wife with Charlie.
David and his Whitney expedition partners Dan and Brian.
Episode Resources:
Apply to the Live Your Dream Grant (Opening March 1st, 2025)
Charles Martin Corvi Fund Website
Deep Survival by Laurence Gonzalez
Resources On Infant or Child Loss:
Healthy Birthday (Stillbirth Prevention Advocates)
The Line: News From the Cascades to the Karakoram
Binocular view of the crux fourth pitch of Borrowed Time on the west face of Sloan Peak. Photo: Michael Telstad.
SLOAN PEAK, BORROWED TIME
The west face of Sloan Peak, about 20 kilometers southwest of Glacier Peak in Washington’s North Cascades, has seen a flurry of winter climbing in the past five years. But one obvious plum remained: a direct route up the center of the face, with an intimidating crux pitch leading past steep rock to a hanging dagger. In January, Northwest climbers Justin Sackett and Michael Telstad picked that plum, climbing nearly 2,000 feet up the west face in a long day. We’re sharing Telstad’s report for AAJ 2025 here.
The west face of Sloan Peak (7,835’) has been at the forefront of my mind for about as long as I’ve been winter climbing. Despite numerous attempts, the main face was unclimbed to the summit in winter until 2022, with the completion of Superalpine (IV WI3/4, Legallo-Roy). In 2023, the Merrill-Minton (a.k.a. The Sloan Slither, 1,600’, IV WI4+) climbed partway up the center of the face, then moved rightward to join Superalpine. A previous winter line on Sloan Peak, Full Moon Fever (IV AI4 R 5.8, Downey-Hinkley-Hogan, 2011), started on the west face then angled up the northern shoulder.
Directly above the point where the Merrill-Minton cuts right to easier ground, a large hanging dagger is guarded by gently overhanging, compact gneiss. Known as one of the biggest unpicked plums in the North Cascades, the direct line past the dagger was going to get climbed sooner or later—it was just a question of by whom and in what style. When a perfect weather window arrived in the forecast, I convinced Justin Sackett to drive up from Portland for an attempt.
The west face of Sloan Peak showing the line of Borrowed Time, climbed in January 2025. The climbers followed the Merrill-Minton Route (2023) up to the middle of the big rock band, then continued straight up where the Merrill-Minton veered right. Photo: John Scurlock.
Early on January 19, 2025, we stepped away from the car and into the rainforest. We reached the base of the route at first light. Following the Merrill-Minton for the first three pitches, we encountered climbing up to WI5 R—a far cry from the moderate ice reported on the first ascent. Below the dagger, we took a short break and got ready for an adventure. I’d chosen to leave the bolt kit behind. This route deserved an honest attempt on natural gear before being sieged.
No bolts on this mixed pitch: Michael Telstad zigzags up overhanging gneiss on the fourth pitch of Borrowed Time, the M7 crux of the route. Photo: Justin Sackett.
After traversing back and forth a few times, I chose my line to the ice and started up. The rock on this portion of the wall is highly featured but compact and fractured. Just about every seam that might take gear was packed full of frozen moss; finding decent protection was a slow, agonizing process. A steep crux near the end of the pitch held potential for a huge fall, but an improbable no-hands rest allowed me just enough of a reprieve to get good gear.
On the summit. Photo: Justin Sackett.
Justin joined me in the sun above the dagger, and we continued up a pitch of perfect blue water ice to snow slopes. Rather than finish via the standard scramble route, we opted for an obvious corner system above us. Reminiscent of Shaken Not Stirred on the Mooses Tooth in Alaska, this narrow slot held steps of water ice broken by sections of steep snow—the ideal finish to an excellent climb.
Arriving on the windless summit around 3:45 p.m., we took a short break and began our descent along the southeast shelf. After what felt like an eternity of steep downclimbing, we post-holed back to the cars, arriving a bit after 8 pm. Our direct new route is called Borrowed Time (1,900’, IV WI5 M7).
RESCUE ON SLOAN PEAK
In a sad footnote to the Sloan Peak story, a climber was severely injured in a long fall on the mountain about a week after the ascent reported above, apparently attempting one of the initial pitches on either this line or the Merrill-Minton route. The climber was pulled from the face in a dramatic helicopter mission—the five-minute video from Snohomish County Sheriff’s Office is a remarkable window into such rescues. We wish the climber well in his recovery.
The third bivouac on the north pillar of Yashkuk Sar I. Photo courtesy of Dane Steadman.
YASHKUK SAR FIRST ASCENT
Crashhhhh! rang through the perfectly still night. To say this woke up August Franzen, Cody Winckler, and me would be a lie. How could we sleep? We were camped below the biggest objective of our lives, on our first trip to Pakistan, alone in the Yashkuk Yaz Valley aside from our two cooks and liaison officer back at base camp, surrounded by the most beautiful, terrifying, inspiring, and chaotic mountains we’d ever seen. Now, on the glacier beneath Yashkuk Sar I (6,667m), about a mile past our advanced base camp, I poked my head out the tent door to see a gargantuan avalanche roaring down the peak’s north wall, its powder cloud billowing toward us.
“Should we run?” asked August.
That’s the start of the article Dane Steadman has written for AAJ 2025. The new AAJ will be mailed to AAC members in September, but you can hear Dane talk about this climb right now in the latest Cutting Edge podcast. Along with Dane’s interview, you’ll hear alpinists Kelly Cordes and Graham Zimmerman, plus AAJ editor Dougald MacDonald, sharing their insights on this climb and the unique challenges and attractions of climbing in the Karakoram.
The 2024 Yashkuk Sar I expedition was supported by a Cutting Edge grant from the American Alpine Club.
The Line is the newsletter of the American Alpine Journal (AAJ), emailed to more than 80,000 climbers each month. Find the archive of past editions here. Interested in supporting this publication? Contact Heidi McDowell for opportunities. Got a potential story for the AAJ? Email us: [email protected].
Your Guide to Climbing at The New River Gorge
Life: An Objective Hazard
Zach Clanton’s Climbing Grief Fund Story
by Hannah Provost
Photos by AAC member Zach Clanton
Originally published in Guidebook XIII
I.
Zach Clanton was the photographer, so he was the last one to drop into the couloir. Sitting on the cornice as he strapped his board on, his camera tucked away now, his partners far below him and safe out of the avalanche track, he took a moment and looked at the skyline. He soaked in the jagged peaks, the snow and rock, the blue of the sky. And he said hello to his dead friends.
In the thin mountain air, as he was about to revel in the breathlessness of fast turns and the thrill of skating on a knife’s edge of danger, they were close by—the ones he’d lost to avalanches. Dave and Alecs. Liz and Brook. The people he had turned to for girlfriend advice, for sharing climbing and splitboarding joy. The people who had witnessed his successes and failures. Too many to name. Lost to the great allure, yet ever-present danger, of the big mountains.
Zach had always been the more conservative one in his friend group and among his big mountain splitboard partners. Still, year after year, he played the tricky game of pushing his snowboarding to epic places.
Zach is part of a disappearing breed of true dirtbags. Since 2012, he has lived inside for a total of ten months, otherwise based out of his Honda Element and later a truck camper, migrating from Alaska to Mexico as the seasons dictated. When he turned 30, something snapped. Maybe he lost his patience with the weather-waiting in Alaska. Maybe he just got burnt out on snowboarding after spending his entire life dedicated to the craft. Maybe he was fried from the danger of navigating avalanche terrain so often. Regardless, he decided to take a step back from splitboarding and fully dedicate his time to climbing, something that felt more controllable, less volatile. With rock climbing, he believed he would be able to get overhead snow and ice hazards out of his life. He was done playing that game.
Even as Zach disentangled his life and career from risky descents, avalanches still haunted him. Things hit a boiling point in 2021, when Zach lost four friends in one season, two of whom were like brothers. As can be the case with severe trauma, the stress of his grief showed up in his body—manifesting as alopecia barbae. He knew grief counseling could help, but it all felt too removed from his life. Who would understand his dirtbag lifestyle? Who would understand how he was compelled to live out of his car, and disappear into the wilderness whenever possible?
He grappled with his grief for years, unsure how to move forward. When, by chance, he listened to the Enormocast episode featuring Lincoln Stoller, a grief therapist who’s part of the AAC’s Climbing Grief Fund network and an adventurer in his own right—someone who had climbed with Fred Beckey and Galen Rowell, some of Zach’s climbing idols—a door seemed to crack open, a door leading toward resiliency, and letting go. He applied to the Climbing Grief Grant, and in 2024 he was able to start seeing Lincoln for grief counseling. He would start to see all of his close calls, memories, and losses in a new light.
Photo by AAC member Zach Clanton
II.
With his big mountain snowboarding days behind him, Zach turned to developing new routes for creativity and the indescribable pleasure of moving across rock that no one had climbed before. With a blank canvas, he felt like he was significantly mitigating and controlling any danger. There was limited objective hazard on the 1,500-foot limestone wall of La Gloria, a gorgeous pillar west of El Salto, Mexico, where he had created a multi-pitch classic called Rezando with his friend Dave in early 2020. Dave and Zach had become brothers in the process of creating Rezando, having both been snowboarders who were taking the winter off to rock climb. On La Gloria, it felt like the biggest trouble you could get into was fighting off the coatimundi, the dexterous ringtail racoon-like creatures that would steal their gear and snacks.
After free climbing all but two pitches of Rezando in February of 2020, when high winds and frigid temperatures drove them off the mountain, Zach was obsessed with the idea of going back and doing the first free ascent. He had more to give, and he wasn’t going to loosen his vise grip on that mountain. Besides, there was much more potential for future lines.
Dave Henkel on the bivy ledge atop pitch eight during the first ascent of Rezando. PC: Zach Clanton
But Dave decided to stay in Whistler that next winter, and died in an avalanche as Zach was in the process of bolting what would become the route Guerreras. After hearing the news, Zach alternated between being paralyzed by grief and manically bolting the route alone.
In a world where his friends seemed to be dropping like flies around him, at least he could control this.
Until the fire.
It was the end of the season, and his friend Tony had come to La Gloria to give seven-hour belays while Zach finished bolting the pitches of Guerreras ground-up. Just as they touched down after three bivvies and a successful summit, Tony spotted a wildfire roaring in their direction. Zach, his mind untrained on how fast forest fires can move, was inclined to shrug it off as less of an emergency than it really was. Wildfire wasn’t on the list of dangers he’d considered. But the fire was moving fast, ripping toward them, and it was the look on Tony’s face that convinced Zach to run for it.
In retrospect, Zach would likely not have made it off that mountain if it weren’t for Tony. He estimates they had 20 minutes to spare, and would have died of smoke inhalation if they had stayed any longer. When they returned the next winter, thousands of dollars of abandoned gear had disintegrated. The fire had singed Zach’s hopes of redemption—of honoring Dave with this route and busying his mind with a first ascent—to ash. It would only be years later, and through a lot of internal work, that Zach would learn that his vise grip on La Gloria was holding him back. He would open up the first ascent opportunity to others, and start to think of it as a gift only he could give, rather than a loss.
But in the moment, in 2021, this disaster was a crushing defeat among many. With the wildfire, the randomness of death and life started to settle in for Zach. There was only so much he could control. Life itself felt like an objective hazard.
III.
In January 2022, amid getting the burnt trash off the mountain and continuing his free attempts on Guerreras, Zach took a job as part of the film crew for the National Geographic show First Alaskans—a distraction from the depths of his grief. Already obsessed with all things Alaskan, he found that there was something unique and special about documenting Indigenous people in Alaska as they passed on traditional knowledge to the next generation. But on a shoot in Allakaket, a village in the southern Brooks Range, his plan for distraction disintegrated.
In the Athabascan tradition, trapping your first wolverine as a teenager is a rite of passage. Zach and the camera crew followed an Indigenous man and his two sons who had trapped a wolverine and were preparing to kill and process the animal. In all of his time spent splitboarding and climbing in these massive glaciated mountains that he loved so much, Zach had seen his fair share of wolverines— often the only wildlife to be found in these barren, icy landscapes. As he peered through the camera lens, he was reminded of the time he had wound through the Ruth Gorge, following wolverine tracks to avoid crevasses, or that time on a mountain pass, suddenly being charged by a wolverine galloping toward him. His own special relationship with these awkward, big-pawed creatures flooded into his mind. What am I doing here, documenting this? Was it even right to allow such beautiful, free creatures to be hunted in this way? he wondered.
The wolverine was stuck in a trap, clinging to a little tree. Every branch that the wolverine could reach she had gnawed away, and there were bite marks on the limbs of the wolverine where she’d attempted to chew her own arm off. Now, that chaos and desperation were in the past. The wolverine was just sitting, calm as can be, looking into the eyes of the humans around her. It felt like the wolverine was peering into Zach’s soul. He could sense that the wolverine knew she would die soon, that she had come to accept it. It was something about the hollowness of her stare.
He couldn’t help but think that the wolverine was just like all his friends who had died in the mountains, that there had to have been a moment when they realized they were going to be dead—a moment of pure loneliness in which they stared death in the face. It was the loneliest and most devastating way to go, and as the wolverine clung to the tree with its battered, huge, human-like paws, he saw the faces of his friends.
When would be the unmarked day on the calendar for me? He was overwhelmed by the question. What came next was a turning point.
With reverence and ceremony, the father led his sons through skinning the wolverine, and then the process of giving the wolverine back to the wild. They built a pyre, cutting the joints of the animal, and burning it, letting the smoke take the animal’s spirit back to where it came from, where the wolverine would tell the other animals that she had been treated right in her death. This would lead to a moose showing itself next week, the father told his sons, and other future food and resources for the tribe.
As Zach watched the smoke meander into the sky through the camera lens, the cycle of loss and life started to feel like it made a little more sense.
IV.
After a few sessions with Lincoln Stoller in the summer of 2024, funded by the Climbing Grief Fund Grant, Zach Clanton wasn’t just invested in processing and healing his grief—he was invested in the idea of building his own resiliency, of letting go in order to move forward.
On his next big expedition, he found that he had an extra tool in his toolbox that made all the difference.
They had found their objective by combing through information about old Fred Beckey ascents. A bush plane reconnaissance mission into the least mapped areas of southeast Alaska confirmed that this peak, near what they would call Rodeo Glacier, had epic potential. Over the years, with changing temperatures and conditions, what was once gnarly icefalls had turned into a clean granite face taller than El Cap, with a pyramid peak the size of La Gloria on top. A couple of years back, they had received an AAC Cutting Edge Grant to pursue this objective, but a last-minute injury had foiled their plans. This unnamed peak continued to lurk in the back of Zach’s mind, and he was finally ready to put some work in.
As Zach and James started off up this ocean of granite, everything was moving 100 miles per hour. Sleep deprived and totally strung out, they dashed through pitch after pitch, but soon, higher on the mountain, Zach started feeling a crushing weight in his chest, a welling of rage that was taking over his body and making it impossible to climb. He was following James to the next belay, and scaring the shit out of himself, unable to calm his body enough to pull over a lip. This was well within his abilities. What was happening? How come he couldn’t trust his body when he needed it most?
At the belay, Zach broke down. He was suddenly feeling terrified and helpless in this ocean of granite, with the unknown hovering above him. They had stood on the shore, determined to go as far into the unknown sea of rock as they could, while still coming back. When would be the breaking point? Could they trust themselves not to go too far?
Hesitantly at first, Zach spoke his thoughts, but he quickly found that James, who had similar experiences of losing friends in the mountains, understood what he was going through. As they talked through their exhaustion and fear and uncertainty, they recognized in each other the humbling experience of being uprooted by grief, and also the ability to process and keep going. They made the decision to keep climbing until sunset, swapping leads as needed. Zach was inspired, knowing how shattered he had felt, and yet still able to reach deep within to push through. With the resiliency tools he had worked on with Lincoln, this experience didn’t feel so debilitating.
Yet resilience also requires knowing when to say no, when something is too much. After a long, uncomfortable bivy halfway up a 5,000-foot rock climb, the two decided to start the long day of rappels, wary of a closing weather window.
Zach Clanton and his dog, Gustaf Peyote Clanton, at Widebird. “He [Gustaf] is a distinguished gentleman.” Photo by Holly Buehler
Back safely on the glacier, the two climbing partners realized it was their friend Reese’s death day. Taking a whiskey shot, and pouring one out for Reese, they parted ways—James to his tent for a nap, and Zach to roam the glacier.
The experience of oneness he found, roaming that desolate landscape, he compares to a powerful psychedelic experience. It was a snowball of grief, trauma, resilience, meditation, the connection he felt with the friends still here and those gone. It was like standing atop the mountain before he dropped into the spine, and the veil between this world and those who were gone was a little less opaque. He felt a little piece of himself—one that wanted a sense of certainty—loosen a little. The only way he was going to move forward was to let go.
He wasn’t fixed. Death wouldn’t disappear. Those friends were gone, and the rift they left behind would still be there. But he was ready to charge into the mountains again, and find the best they had to offer.
Support This Work—Climbing Grief Fund
The Climbing Grief Fund (CGF) connects individuals to effective mental health professionals and resources and evolves the conversation around grief and trauma in the climbing, alpinism, and ski mountaineering community. CGF acts as a resource hub to equip the mental health of our climbing community.
Sign Up for AAC Emails
The Height of Mountains
EDUCATE: Climbing Gear Innovations, Then and Now
This episode is for the gear nerds out there. The climbing world loves to reminisce on some of climbing’s great inventions of the past, but what’s happening in gear innovation right now? We put together some brief interviews with innovators past and present, to dive into tinkering in the climbing world, then and now.
We’ll start with an excerpt from Yvon Chouinard’s "Legacy Series" interview to hear him reflect on revolutionizing the ice axe. Next, we’ll take a massive leap forward into present-day sport climbing tactics, and chat with Will McNeill, of HangDog Climbing, whose ultralight clip-up device is becoming all the rage in the world of sport projecting. Next, we’ll chat with Brent Barghahn, of Avant Climbing Innovations, about squeaking out the last bit of efficiency for rope soloing systems and hard trad climbing. Then, we’ll take a step back in time again, and chat with Jack Tackle about the late John Middendorf’s legacy in innovating the A5 portaledge, to set us up for our last conversation, a discussion with Nathan Kukathas of Grade 7 Equipment. Nathan is known for inventing the G7 Pod, which many say has been one of the biggest innovations for alpine climbing in years.
Through it all, we’ll talk about inspiration, what it takes to innovate in the climbing gear space, what could be next for climbing gear, and lots and lots about textiles, 3-D printing, and climbing harder.
Episode Resources:
The Prescription—Top-Rope Solo
Angel Wings in Sequoia National Park. Valkyrie (V 5.11+) climbs the sunlit buttress to the right of the highest summit in this image. Photo: Brandon Thau
In this month’s Prescription, an expert climber made two crucial errors in her rope ascension/top-rope solo system. She fortunately escaped with relatively minor injuries.
This accident was featured in the 2024 Accidents in North American Climbing.
Top-Rope Solo Fall | Device Jammed By Sling
Sequoia National Park, Angel Wings
Valkyrie takes the spectacular red line shown above. Clark’s accident occurred on the slab at the bottom of the climb. Photo: Brandon Thau
On October 8, 2023 Whitney Clark was ascending a fixed rope at the start of Valkyrie (17 pitches, 5.11+) when her single ascension device was jammed by a sling. She fell 30 feet to the ground.
Clark wrote to ANAC:
“We woke at around 6 a.m. and made our way to the fixed line from the day before. The days were short and we had many pitches to do. My partner, Luka Krajnc, went first, using a Grigri to jug and then transitioning to climbing. About 40 feet up, he clove-hitched the rope to a bolt. I then started jugging with a single Micro Traxion. Thirty feet up, I leaned back on the rope. My body weight wasn’t supported because the sling around my neck [part of the top-rope solo setup] got sucked into the device and caught in the teeth of the Traxion. The rope was sliding against the sling. I hadn’t tied a backup knot.”
Clark attempted to wrap the rope around her leg. But her rope was new, thin, and slippery. She wrote, “I grabbed the rope and slowly started sliding down. Eventually the rope burn was too painful and I let go. I hit the ground, landed on my feet, and fell backward. I struck my lower back and then my head. I was wearing a helmet. Because the ground was angled, some of the force was dissipated, though I landed six inches from a large rock spike.
“I never lost consciousness but was in a bit of shock. Luka rappelled down and did a spinal exam. He got me comfortable, and I sat there for a while. I had pain in my back and my left ankle. I used my inReach to call for a rescue while Luka retrieved our stuff. I started crawling and butt-scooting to where a heli could reach me. I would have loved to have self-rescued, but it’s a 16-mile hike out. It took about 2.5 hours of crawling to make it to a flat place. Four hours later, a helicopter airlifted me to the Visalia Level III trauma center.”
Whitney Clark’s progress-capture device failed when the as-yet-unused retention sling got stuck in the device as she was ascending. It is common practice to use a sling and an elastic connection to hold the progress-capture device upright as one climbs along a fixed rope. Photo: Luka Krajnc
The Prescription—Video Analysis
Top-rope soloing is becoming increasingly popular. In this video, Pete Takeda, Editor of Accidents in North American Climbing, and IFMGA/AMGA guide Jason Antin are back to provide an accident analysis and give you some quick tips on how to mitigate risk when top-rope soloing.
Top-rope soloing is an integral part of modern climbing. Currently, only one device (the El Mudo) is designed and commercially available for top-rope (and lead) soloing. There are many ways to configure these systems and we’ve demonstrated one possible solution here.
ANALYSIS
Solo top-roping allows a climber to self-belay when no partner is available, for a team to work on individual sections of a route without the need for a belayer, or for two climbers to move simultaneously, as in this situation. The errors Clark made were using only one device to safeguard her progress and not tying a backup knot.
“I was jugging by pulling on the rope, syncing up the slack, and sitting back,” Clark said. “The route was meandering and the fixed line didn’t allow me to readily climb, so I decided to jug straight up the initial blank slab. The sling around my neck was going to hold the Traxion upright [allowing the rope to feed freely] once I started climbing. I haven’t done any top-rope soloing since the accident. I probably will at some point, but I will definitely use two devices. This was the first time I only used a single progress-capture device.” (Source: Whitney Clark.)
Support Our Work—Join the Club
Each membership is critical to the AAC’s work: advocating for climbing access and natural landscapes, offering essential knowledge to the climbing community through our accident analysis and documentation of cutting edge climbing, and supporting our members with our rescue benefit, discounts, grants and more. Plus, get the new 2025 member tee!
Sign Up for AAC Emails
Keenan Griscom is Doing Everything Your Parents Tell You Not To Do
Keenan Griscom giving it his all during the 2023/2024 competition season. Photo courtesy of the UIAA
Every year, ice climbers flock to the Ouray Ice Festival to test their skills on the human made ice flows in the park. A select few test their skills on the ice climbing competition wall. Routes are created that include ice, rock, and plywood in the Scottish Gullies section of the ice park.
The American Alpine Club sat down with USA ice climbing competitor Keenan Griscom. Griscom was rocking a North Face leopard-print 1996 retro Nuptse puffer and Y2K gray wrap-around sunglasses, as chill as the ice around us. We chatted about growing up competing in ice climbing competitions, his new link up Tommy's X (5.14b) in Clear Creek Canyon's Nomad’s Cave, and his experimental competition headspace. The experiment succeeded clearly, since Griscom took home the gold in the Ouray men's lead finals the next day.
AAC: You were the youngest American to win the Ouray Elite Mixed Climbing Competition at age 16. When did you start climbing? How did you get into competitive ice climbing?
Keenan Griscom: My dad actually started me ice climbing when I was four or five here in Ouray. So I've had tools for a long time. And then through Marcus Garcia, [I] found the competition scene and got hooked. I was doing rock comps, and the community in the ice climbing comps was just, so, so good and supportive and friendly, so, as someone who's already into competing, starting the ice comps is just like, oh, this is it. This is a cool spot to be in.
AAC: What was it like competing at such a young age?
KG: I don't know, I've been competing since I was nine. It was somewhat second nature. I've always wanted to give it [my] all in the comps. And Ouray was really special because when I started, there weren't any age categories. It was just the open format, and anyone could sign up. So if you were in, you're competing with everyone. My first two seasons, I didn't place particularly well. But it was so cool to be competing with people like Will Gadd and Ryan Vachon and all these epic mixed-climbers and alpinists who I looked up to.
AAC: What drew you to continue doing competition ice climbing while you fell away from competition bouldering and rock climbing?
KG: I stopped competing in rock comps mainly because the scene isn't as welcoming. There's a lot more toxic competitive nature there, and a lot of people get really worked up and will take other people down to get a better result. There's not really any of that in the ice climbing crew. Ice climbing comps are really fun. I'm going to stick with that. But I've been rock climbing outside nonstop.
AAC: On that note, I noticed you put up an alternative finish to Tommy's Hard Route (5.13d)—Tommy's X (5.14b). What is the relationship between route development and ice climbing? How do those two things relate, if at all for you?
KG: They don't relate a ton since I haven't really done much development for ice or mixed. I've gotten a lot of help from mentors like Marcus, who I met through ice climbing, to teach me development ethics. That route, specifically, it's in a cave near my house, and there's a lot of link ups. I didn't put in any new bolts [for Tommy's X] it was just a new line that hadn't been done yet.
AAC: And what inspired you to do that?
KG: Tommy's Hard Route (5.13d) is an old school natural line in a cave that's almost all manufactured. There is this really, really big dead point crux that I always thought was super, super interesting. Then it's over. You do this really gnarly dead point, and it's jugs to the chains. Which is nice, but more sustained climbing is more my style. There's this other route called Predator X (5.13a/b) that comes in from the left and finishes basically directly above that dead point. And one day, I was wondering if I could link those up, and then it'd be like a perfectly straight line of bolts through the wall. Yeah, it ended up being a really interesting crux sequence after the initial crux.
AAC: That's awesome. You also boulder, can you tell me a little bit more about that?
KG: Yeah, I grew up almost exclusively sport climbing, and then started to do a little bit of bouldering through friends and kind of got hooked on it, because it’s a little bit easier. You can go out and solo sesh a lot of stuff in Clear Creek Canyon near the crib. I took that and ran with it. I've been doing more bouldering than sport lately, and that's currently what I'm probably most excited about, pushing bouldering grades.
AAC: Do you have a preference between sport climbing, bouldering, ice climbing, ice climbing competition, and mixed climbing?
Keenan Griscom is all about staying chill, captured during the 2023/2024 competition season.
KG: Really hard to say. I might put bouldering at the top, but then it's a massive tie for second. Ice climbing comps are unbeatable. There's no other scene that's as fun and welcoming, and the movement is so dynamic. You just don't get the same movement on rock. It's a really fun change of pace. With actual ice and mixed I'd really like to get into doing some more big things and exploratory multi-pitch in [Rocky Mountain National Park]. But I've definitely been more focused on competition and rock climbing lately.
AAC: What does training look like for you?
KG: It depends. This year has been more casual—been working on a lot of power, strength, and technique. Last season was a pretty full-on training block. I basically trained from August through December, like super structured for the World Cup tour, and it ended up panning out really well.
AAC: It definitely did, you received the overall World Cup lead medal in silver, last year. What about competition ice climbing sparks inspiration or joy for you?
KG: Initially, it's like basically everything your parents tell you not to do. You get to jump around with blades on your feet and in your hands and take massive falls in the air. Honestly, on the World Cup scene, it's all a massive party. Everyone's a big family. I find the movement really fun. It's really physical. So you get to actively try hard while you're doing it, which is a good feeling. Honestly, it's the community, like the scene is so fun. That's a large part of why I'm here.
AAC: Who do you think you are as an ice climbing competitor?
KG: I'd like to say Keenan is just a climber who wants to do it all. In ice climbing comps, I'd like to be seen as someone who's really focused on doing as well as they can. But I've done some coaching in Boulder at the Ice Coop, and for me to, like, not feel the stress of the competition, I tend to try and help everyone; making sure everyone else is doing good helps me a lot with not worrying about how it's gonna go. So I guess I would like to be seen as someone who's a wealth of knowledge to come and get help from. But at the same time, I'll put my headphones in and lock in for the warm-ups.
AAC: Who are you outside of climbing?
KG: Outside of climbing, I'm trying to be an artist. I'm wrapping up my Arts Associate right now. I'm a little unsure of what I'm doing afterwards, but I'll figure it out.
AAC: What mediums do you work in?
KG: Fashion and then dry mediums, so, charcoal and graphite.
AAC: What do you hope to get out of this 2025 season?
KG: I'm really excited to go into it with a casual mental space. I'm trying to just put it all on the line during the competitions. I haven't done as much training and prep for this season. I'm trying to play around with different approaches to the competition headspace. Instead of treating it as a competition, I want to treat it as redpointing a project. The goal is not to get a certain placement, or even do well in the comp. The goal is to top the routes. At a world cup level that almost always means winning. It's not like I want to win to top the route, I just want to top. Topping is the main objective.
AAC: What has been the most pivotal moment in your climbing career?
KG: In competition climbing, it was definitely my last season as a U16. I won that year's Youth World Cup. The whole prep I was focused on winning, and when I won, it wasn’t very fulfilling. I felt pretty hollow. That drastically changed how I approached my whole preparation and training. I think that was a massively positive moment.
[For] rock climbing it's really hard to say. I think potentially [when I stopped] competition rock climbing, because I grew up doing camping trips to Indian Creek and Vedauwoo and following leads all the time. And taking a step away from the competition rock was really nice and refreshing to go back to the routes and try really hard on rock without any external things happening.
AAC: If you could be any climb, what would it be and why?
KG: I have two lines in mind. Biographie (9a+/515+) in Céüse, France, because it is the most beautifully perfect chunk of rock I have ever seen. It just looks so incredible—proper dream line. Or Off the Wagon (V14), that V14 in Switzerland. The beta on that thing is the definition of swagger. It's so cool.
AAC: Could you elaborate on that, and leave us with some climbing beta humming around in our heads?
KG: Yeah, the history of that boulder is pretty sweet. Dave Graham and Chris Sharma tried it forever ago, and it's this massive right hand dead point for this first move and then you do a campus row sequence. And that's it. It's a two move V14. It's smash, hold, campus, done. It's in this beautiful little meadow valley in Switzerland, and you start on a wagon. It's a really cool chunk of rock. It's like a perfectly flat 45 degree panel.
Just one podium among many. Keenan Griscom celebrating his bronze medal in the 2024 Champagny Continental Open. Photo courtesy of the UIAA
For the Ouray Competition men's results, click here, and for the women's results, click here. The Ice Climbing competition scene returns to Colorado for the World Cup in Longmont on Feb. 22-23. Watch Team USA compete this February, or learn more about getting involved here.
Want more ice climbing content? Check out A Little Extra Spice: Stories from the World of Competition Ice Climbing
The Line: Exploring Zanskar
“In recent years, the peaks of Zanskar have seen increasing popularity with mountaineering expeditions. Despite this, there are still plenty of unclimbed summits from 5,500m to 6,500m….”
That’s the start of a report for AAJ 2025 from Matic “Matija” Jošt from Slovenia, who has completed four exploratory expeditions to Zanskar, in the southwest of Ladakh, India, in the last decade. Jošt’s detailed, photo-rich trip reports have prompted a lot of recent activity (including three additional reports in the upcoming AAJ). Below, we offer highlights from Jošt’s latest exploration, plus a brief Q&A with the man himself.
The view from around 5,200 meters above the Chhogo Tokpo. At left is the south summit of T16, climbed in 2016 by Cosmin Andron and Cristina Pogacean from Romania. The main summit of T16, climbed in 2024 and named Skarma Mindruk Ri, is hidden to the left. At right is unclimbed T13 (6,436m). Photo by Matic Jošt.
Chhogo Tokpo, Four First Ascents
“Uroš Cigljar, Tilen Cmok, Boštjan Dečman, Nejc Škrablin, Tomaž Žerovnik, and I arrived on July 7 at base camp in the Chhogo Tokpo, the eastern branch of the Haptal Tokpo. [Tokpo is a word for “valley” in this area of India.] While several parties had visited adjacent valleys and climbed a few peaks on the watershed ridges with the Chhogo, the only reported climbing expedition to visit the Chhogo valley was an Indian-Romanian team in 2016 that climbed one peak and attempted another (AAJ 2017).
“A very complex 6,431m mountain known as T16 was our main objective. [Peaks above various Zanskar valleys were numbered by Kimikazu Sakamoto, whose teams made exploratory expeditions in Zanskar from 2009 to 2016; Sakamoto published the first climber-friendly topographical sketches of these mountains.] The lower south summit was climbed by Romanians Cosmin Andron and Cristina Pogacean in 2016, but the easiest approach to the main top appeared to lie up the south slopes above the Khapang Glacier, east of the Chhogo valley. The big riddle was finding a suitable passage from the Chhogo to the Khapang, and we decided to devote part of our acclimatization to solving this problem.
The final ascent to Skarma Mindruk Ri (6,431m), the peak formerly known as T16. Photo by Matic Jošt.
“Aiming for a col on the ridge south of T16, we hiked up a side glacier, passing the route climbed by the Romanians, and climbed a 300m west-facing gully (300m, D+ 60° M3) to reach the col (5,836m). From there, it would be easy to descend to the gentle Khapang Glacier and traverse over to T16’s main peak.
“The whole team returned to the col camp on the 14th, and the next day, in perfect weather, we climbed south-facing slopes above the Khapang Glacier and along the east ridge to the summit of T16 (600m, D+ 60°). Our expedition had been organized by a club from the Slovenian town Šentjur, so we named our route Šentjurka (900m, D+). We later encouraged people in the nearest village, Tungri, to suggest a name for the peak, and they came up with Skarma Mindruk Ri. (Skarma is “star,” and Mindruk is a specific star in the constellation of Pleiades.) Maybe the name will catch on.”
Boštjan Dečman and Nejc Škrablin on the upper Khapang Glacier. The col they crossed to reach the glacier is just left of Škrablin. The huge rock fin behind leads to unclimbed T13 (6,436m). In back on the left is unclimbed Peak T11 (6,177m). Photo by Matic Jošt.
Later in this expedition, Jošt and Žerovnik crossed a different col to reach the Korlomshe Tokpo, where a British team in 2015 had attempted what they called a “Matterhorn-like peak.” The Slovenians climbed the east face and south slopes to reach the 6,130m summit. “We named the route Charlatan De Balkan (500m, D+ 60° ice) after an album by a popular Slovenian group,” Jošt writes. “As the peak was absolutely nothing like the famous Swiss mountain, we named it Antimatterhorn.”
Team members also attempted the west face of unclimbed Peak 5,435m, close to base camp, and made the first ascent rock tower east of camp, which was dubbed Ibex (5,321m).
Below the east face of the Antimatterhorn (6,130m). Photo by Tomaž Žerovnik.
By July 24, most of the party had left base camp. “Although I’ve been climbing around 45 years, I don’t have much experience with soloing, but I decided to try the north face of T9 (6,107m), which I had seen from the Antimatterhorn approach,” Jošt writes in his report. “I left base camp at 1 a.m. on the 25th, carrying two axes but no rope. The north face became icier and brittle the higher I climbed, but at 8:30 a.m. I reached the west ridge. The upper section of this ridge was rockier, but in one hour I was standing on the summit.” Uncomfortable with downclimbing the north face he had ascended, he headed down a couloir on the southwest face to a neighboring glacier, traversing the mountain, and made it back to base camp by 3 p.m.
“The locals suggested the name Spao Ri for the peak. It means “brave mountain.” I named the route Old and Abandoned (700m, TD II/III 75° ice). Why? Because I’m not young anymore.”
Jošt’s comprehensive report from the 2024 expedition, including some general notes on climbing in Zanskar, will be available at the AAJ website later this year. To see a copy sooner, email [email protected].
—Matic Jošt, Slovenia
Four Questions
Matic Jošt, 55, first appeared in the AAJ in 1996 as a member of a Slovenian expedition to Gasherbrum I. His expeditions have taken him to high mountains throughout Asia, as well as climbs in Peru.
Jošt climbing the north face of Planja in the Julian Alps of Slovenia. Photo by in Matjaž Dušič.
Q. Where do you live in Slovenia and what do you do for work there?
A. At the moment, I mostly live close to Celje in the central part of Slovenia. I am a self-employed engineer. In 2021, I applied for the IFMGA guide course and probably will finish this summer. So, last year I earned some money as an aspirant guide, too. I also sometimes do rope access work.
Q. What is it about Zanskar that keeps luring you back?
A. Easy logistics and some unexplored areas, nice local people. The mountains are not so high, and I can find easily something that fits my ambitions. It is not too expensive, and I can afford it. And after all, I am quite familiar with the geography of the region.
Q. Are there issues with climbing there?
A. The lack of quality maps in the area has partly been mitigated by navigation applications, but there is still confusion regarding peak names and, over the years, a general lack of systematic recording of activity. The IMF (Indian Mountaineering Federation) has a list of open peaks that includes geographical coordinates and altitudes, but they simply number the peaks; very few mountains on the list have names.
I also think the IMF expedition policy for foreigners and their system based on “peak permissions” is out of date and quite inappropriate for such areas as Zanskar and other mountain ranges north of the main Himalayan divide. A more suitable management model would set boundaries within which climbers could choose any peaks they want to attempt.
Q. Other than your trips to India, what have been your favorite international expeditions? And where is your favorite place to climb at home?
A. All of my expeditions are my favorite. I am happy that from all the expeditions which I have participated in, we all came home alive. We have had some close escapes, accidents, and injuries, but we had luck. At home I really like Ojstrica (in the eastern Kannik Alps). It has nice north face above Logarska dolina (valley) to climb in summer, and nice southern slopes for skiing in winter. I also sport climb as much as I can to keep my fitness.
The Line is the newsletter of the American Alpine Journal (AAJ), emailed to more than 80,000 climbers each month. Find the archive of past editions here. Interested in supporting this publication? Contact Heidi McDowell for opportunities. Got a potential story for the AAJ? Email us: [email protected].
Sign Up for AAC Emails
The Prescription—Bouldering Fall
Photo by AAC Member Merrick Ales
It’s bouldering season in Hueco Tanks, Texas. While most consider bouldering relatively safe, it is perhaps the most accident- and injury-plagued facet of climbing. This month we bring you an accident that took place in 2024 on a famous John Sherman highball called See Spot Run.
This accident will be featured in the 2025 Accidents in North American Climbing.
Bouldering Fall | Poor Pad Placement
Hueco Tanks State Park, North Mountain
Hueco Tanks is a world-class climbing area known for its outstanding bouldering. It’s also known for having more than its fair share of spicy highball problems. Photo: Pete Takeda.
On January 22, I (Pete Korpics, 35) was attempting to climb a long-standing project of mine called See Spot Run (V6). I was well aware of the risks involved and that it would require ample padding.
During previous sessions, I had placed six or more pads in a wide area including the back of the fall zone. Six pads or more is ideal, but I was admittedly negligent on the day of the accident, as I felt I’d complete the route and was excited to do it. I also felt that the pad number and pad placement—five total and not as wide as prior attempts—was adequate, given the presence of two spotters. I felt very strong getting to the crux. After pulling through the crux, I got very pumped, lost momentum, and hesitated. We all know that moment when you feel uncertain about the next move. In those moments we tell ourselves, “Do it anyway.” Sometimes this works, but often it doesn’t. In this case, I fell.
I fell from roughly 15 feet up, with quite a bit of force. My spotters were hesitant to put their bodies in harm’s way. I had told them that, above the crux, staying clear was the best thing to do. Having two people injured is worse than one.
Due to the momentum of the fall and the poor pad placement, my left foot hit the rock and right foot hit the pad. I severely sprained my ankle. It was probably not helpful that it has in the past received the same injury.
Pete Korpics on an early attempt on See Spot Run. He recalls, “I was very familiar with this famous and dangerous route, as I’d been attempting it for several years.” Photo: Pete Takeda.
ANALYSIS
Bouldering is inherently dangerous, and highball problems particularly so. Besides being a four-star John Sherman classic, See Spot Run is a notorious ankle breaker. It is 25 feet tall and described on Mountainproject.com as “one of the more notorious highball problems at Hueco.”
During the same season that Korpics had his accident, other falls from the route caused multiple ankle sprains.
Keep ‘Em On The Pad!
On highballs, the impact forces of a falling climber can be equally hazardous to the spotter. The general rule for highballs (and all bouldering for that matter) is to ensure that the falling climber lands on the pads and stays on the pads after impact. Spotting might look less like controlling and guiding the fall, and more like giving the falling climber a shove to keep them on the pads. The spotter(s) should also protect the head and neck from striking bare ground, rocks, etc.
Korpics wrote to ANAC: ”Preventable action would have included better pad placement and more pads. We could have used thinner pads to cover gaps between pads. This accident may also have been prevented by assertive spotting, and a strong shove from one of the spotters would have landed me on the pads. That possibility was negated because I had instructed my spotters to stand clear if I fell from above the crux.
“Confidence should not lead to complacency,” he continued. “I’d been climbing a lot and climbing well, including numerous highballs prior to the accident, so I’d let my guard down. I do not blame the spotters, as I had given them specific instructions. I had placed the pads, I chose to climb despite knowing more pads would be better, and the injury was my fault.”
(Sources: Pete Korpics, Mountainproject.com, and the Editors.)
Sign Up for AAC Emails
Celebrating AAC Member Bill Atkinson's 100th Birthday
Provided by Holley Atkinson.
Climbing is a powerful force that connects us. Even when climbing takes a backseat in our lives, we are still connected to the people we have partnered with, the places we have climbed, and the impact we have had.
Today, we celebrate the 100th birthday of one of our members, Bill Atkinson. Bill started climbing in the Shawangunks in the late 50's and joined the American Alpine Club in 1978. He was the New England Section Chair and was awarded the Angelo Heilprin Citation Award in 2006 for exemplary service to the Club. He is one of our oldest members and has been a member of the American Alpine Club for 47 years.
Happiest centennial to you, Bill!
Below, you'll find reflections from climbers celebrating Bill's incredible impact and character:
PC: Chris Vultaggio
Bill, your presence in our climbing world has been productive and prolific—and your life has been the same! Your postings have always been inspiring. Thanks for doing all of those. Some segments should be required before being granted membership in the AAC!
We never climbed together – except at the Annual AAC New England Section and some Annual Dinners. That is to say, climbing up to the bar. I'm fifteen years younger, so you were out there ahead of me. But I have you beat on one score! I climbed Mt. Sir Donald via the same route you took, but back in 1962. I was also in the Bugaboos that summer.
You'll be getting a lot of these postings, so I'll keep this short. Thanks again for all you've done for our world. Happy Century! Hang around for another 15 so you can help me celebrate mine.
–Jed Williamson
Happy Birthday, Bill,
You are one very special person, a thoughtful, helpful climber with such an important history of climbing in New England. I respect you and your contributions to the AAC and climbing. Hats off to you, young man. I salute you for your many contributions.
Thank you, and special wishes every day.
Happy Birthday,
Bruce Franks
Rick Merrit celebrates Bill's Birthday by remembering the times they connected through climbing…
Bill was a great section leader as I became more involved in the AAC. He worked hard to recruit and recognize new members through our section's formal dinners. I remember climbing with him on White Horse Ledge in North Conway when he was in his 80s. I also remember hiking with Bill and his friend Dee Molinar when the ABD was at Smith Rock.
Warm regards to Bill,
Rick Merritt
I mainly know Bill through the AAC, specifically the New England chapter, which Bill energetically chaired for many years. We all looked forward to the wonderful black tie annual dinners held in the old Tufts mansion in Weston, MA, that he so carefully organized.
I always enjoyed listening to Bill's extraordinary life experiences, like when he served as a radar navigator in a B52 in the Pacific during WWII, or marveling at his many fascinating inventions and creations, like the beautiful chess boards he crafted and, of course, his amazing climbing career. Bill remained extremely active as a climber long after most of his peers retired, and I remember he climbed the Black Dike when he was 80, I think! That may have been the oldest ascent ever!
I've always appreciated Bill's kind, soft-spoken character and the interest he always showed in others. Bill is a true Renaissance man, and I feel fortunate to know him.
Happy 100th birthday, Bill!
What a milestone!
–Mark Richey
The Line: Ascents for the Ages
Babsi Zangerl high on Free Rider during her first flash ascent of El Cap. Photo by Miya Tsudome for Highpoint Productions.
BABSI ON FREE RIDER—THE PODCAST
Babsi Zangerl’s flash ascent of Free Rider on El Capitan in November—the first flash of any El Cap big-wall free route—was a highlight of the year in climbing. In the new Cutting Edge podcast, the 36-year-old Austrian climber describes her preparation, fears, and the intense effort of her no-falls ascent of the 5.13a wall. Plus, Alex Honnold, Josh Wharton, and AAJ editor Dougald MacDonald add personal perspective and context on Babsi’s historic Free Rider ascent. Listen to the new episode here!
Yawash Sar I (6,258m) in far northern Pakistan. The round-trip from base camp took seven days. Photo: Janusz Majer.
FOWLER-SAUNDERS IN PAKISTAN
Two of the most accomplished and adventurous climbers of the modern era are Mick Fowler, a retired tax inspector for Great Britain’s revenue department, and Victor Saunders, a U.K. architect turned Chamonix mountain guide. The two completed their first major new route in Pakistan together 37 years ago. This past autumn, Fowler, now age 68, and Saunders, 74, completed another big new route: the first ascent of a 6,258-meter peak, also in Pakistan. Read on to learn more about both climbs.
YAWASH SAR I, FIRST ASCENT
Victor Saunders (left) and Mick Fowler in Pakistan. Photo by Mick Fowler.
In September 2024, Victor Saunders and I made the first ascent of Yawash Sar I (6,258m), a shapely peak at the head of the Koksil (a.k.a. Shop Dur) Glacier in the Ghujerab Mountains, very near the frontier with China. [In 2022, a British team made three attempts on the south face and southern ridges of Yawash Sar I, on the opposite side of the mountain. (See AAJ 2023.) No prior attempt from the Koksil Glacier, which drains to the northwest, has been reported.]
Victor and I met in Islamabad on August 26, flew to Gilgit, spent a night in Karimabad, and arrived at Koksil (ca 4,000m), 12 kilometers west of Khunjerab Pass on the Karakoram Highway, on the 28th. Bad weather delayed us for a day, but on the 30th, after one day of walking, we established a base camp at around 4,600 meters on the highest grassy meadows below the Koksil Glacier.
You call this a retirement home? Fowler at the cramped first bivouac on Yawash Sar I. Photo by Victor Saunders.
The weather was unstable over the period from August 31 to September 9. However, we were able to make a reconnaissance of the approach to Yawash Sar and get good views of its north and northwest flanks. During this period, to aid acclimatization and get more views of Yawash Sar, we ascended Peak 5,636m, first climbed by a Polish-Italian team in 2011 (see AAJ 2012).
On September 10, we left base camp to attempt our main objective. That day we walked up the main Koksil Glacier to camp at a point below the 5,426m West Yawash Col. On the 11th we climbed through an icefall to gain the previously unvisited glacier basin between Yawash Sar I and Peak 6,072m.
The west-northwest face of Yawash Sar I has three groove/couloir lines. We climbed the central one. On September 12, we crossed the bergschrund and were pleased to find excellent conditions. Once established on the line, we climbed thin ice runnels to a bivouac at about 5,750m. There was a notable dearth of good bivouac sites, and we had to traverse about 35m out of the couloir to a point where we were able to fashion a ledge on a sharp rock crest. On the 13th, we climbed more thin ice streaks and mixed ground to meet the southwest ridge at about 6,050m. Here, we endured a very uncomfortable and windy sitting bivouac.
Saunders arriving at a belay on Yawash Sar I. The high summit on the left is unclimbed Peak 6,072m. Photo by Mick Fowler.
On the 14th the weather deteriorated, and it began to snow. We traversed left across a rock wall (where we’d been concerned we might be stopped) and gained the summit slopes, which we followed to the top, arriving at around 11 a.m. We stayed about five minutes and then rappelled all the way to the bottom of the face, reaching the glacier at about midnight on the same day. On the 15th and 16th, we returned to base camp.
The upper reaches of the Koksil Glacier had only been visited by one previous party, the Polish/Italian team noted above, and numerous possibilities for climbers remain.
— Mick Fowler, U.K.
Much of the Golden Pillar of Spantik consisted of thin ice or powder snow over marble slabs, making for long runouts and very insecure climbing. Photo by Victor Saunders from AAJ 1988.
THE GOLDEN PILLAR OF SPANTIK
If the Piolets d’Or had existed at the time (they didn’t debut until 1992), Mick Fowler and Victor Saunders’ ascent of the Golden Pillar of Spantik (7,027m) in 1987 surely would have earned them a golden ice axe. Their six-day climb of the 2,100m northwest face was a landmark of late-’80s alpinism, with bold climbing in unstable weather on a stunning formation, followed by a nerve-wracking descent on uncharted terrain. Here’s an excerpt from Saunders’ article in AAJ 1988, describing day four of the climb:
Photo from AAJ 1988 by Victor Saunders.
“By midday, we reached a large flat ledge, the top of a giant jammed block. There we made tea and relaxed until it occurred to us to look up. We were completely surrounded by overhangs. Fowler led an aid pitch to gain the lowest of a series of ramps. The lower ramps led to a shield, which was the other area of uncertainty for us. From Base Camp there had appeared to be no line around this feature, but a hidden chimney revealed itself at the end of the ramp. Because it was blank-sided and there was no belay at the top, I had to belay Mick by wedging my body across the chimney and asking him not to fall.
“I do not remember having a more miserable bivouac than the one we had that night. We were benighted and there was no ledge, nor even the possibility of cutting one on the thin ice. We used the tent as a hanging bag, inside of which Mick spent the night in his harness, while I stood in my rucksack. It snowed all night.”
There’s much more to enjoy in this classic AAJ story: Read it here. To see the story in its original format, download the PDF (icon in upper right of the web page.)
FOWLER AND SAUNDERS: FURTHER READING
Fowler and Saunders have published many articles and books, replete with wild adventures and Brit-style self-deprecating humor. For tales from Fowler’s early years, turn to his 1995 book Vertical Pleasure: The Secret Life of a Tax Man. Saunders’ 1990 book Elusive Summits (winner of Britain’s Boardman Tasker Prize) is probably his best. Both books describe the landmark Spantik ascent.
The Line is the newsletter of the American Alpine Journal (AAJ), emailed to more than 80,000 climbers each month. Find the archive of past editions here. Interested in supporting this publication? Contact Heidi McDowell for opportunities. Got a potential story for the AAJ? Email us: [email protected].
CLIMB: Behind the Scenes of the Cutting Edge Grant, with Jack Tackle
In this episode, we sit down with legend Jack Tackle to discuss all things cutting edge. We begin by diving into the many first ascents of Jack’s own alpinism career, his progress as a climber, and his deep history with the AAC. We cover the evolution of adventure grants in climbing, how the AAC’s Cutting Edge Grant got started, and why it’s the premiere climbing grant in today’s climbing scene. We also cover the last few years of successes that have come out of Cutting Edge Grant expeditions, a behind the scenes look at some of the considerations these alpinists face when pursuing such high-end objectives, and how Jack’s experience can shed light on the significance of these ascents. Plus, we cover some of the other AAC grants and how they meet the needs of climbers at all levels.
We don’t cover the exact details of the expedition planning process, or how important it is for these expeditions to be respectful and cognizant of both local cultures and environmental issues, or what happens when things go disastrously wrong. That’s for another episode!
If you love following the cutting edge of climbing, or are considering applying to the Cutting Edge Grant yourself this year, or want to soak up Jack’s wisdom, this dive into the history and present of adventure grants is a fascinating look at the logistics it takes to pursue the cutting edge!
You still have time to apply to the 2024 Cutting Edge Grant, presented by Black Diamond! Apply before midnight on Dec 31, 2024.
EXPLORE Act Passes and NPS Discontinues Fixed Anchor Proposal
Wrapping up after a long day of work. AAC Member Andy Cochrane.
It has been a momentous week for climbing policy, and we want to thank all of you who shared your voices with your legislators on these matters. The EXPLORE Act, which the AAC and its partners have been working on in some form or another for nearly 10 years, passed with unanimous consent, and is awaiting a presidential signature as we speak. Secondly, the National Park Service announced late Wednesday afternoon (December 18th) that they were discontinuing the development of their proposed fixed anchor guidance.
What does this mean for climbers?
The EXPLORE Act:
The EXPLORE Act, introduced by Rep Bruce Westerman (R-AR) and Rep Raul Grijalva (D-AZ), is a historic recreation package that has had widespread bipartisan support and support from outdoor recreationists of all stripes—including climbers, mountain bikers, hunters, anglers, and more.
The most important elements of the EXPLORE Act for climbers are two-fold.
First, EXPLORE includes the Protecting America’s Rock Climbing (PARC) Act, introduced by Rep. Joe Neguse (D-CO) and Rep John Curtis (R-UT). The PARC Act is intended to ensure safe and sustainable access to rock climbing in designated Wilderness areas. It requires federal agencies to recognize recreational climbing as an appropriate activity in accordance with the Wilderness Act of 1964, as well as recognizing that the placement, use, and maintenance of fixed anchors is appropriate. The act also ensures that a public comment period is made available prior to any final climbing management guidance being issued. Essentially, the PARC Act officially recognizes that the use of fixed anchors for climbing (and Search and Rescue operations) continues to be appropriate in Wilderness areas, provided it does not diminish the wilderness character of the area.
Second, EXPLORE includes the Simplifying Outdoor Access for Recreation Act (SOAR Act), which will increase accessibility to the outdoors by improving recreational permitting for outfitters and guides. How? By:
Streamlining the process of issuing permits to guides and outfitters
Make more recreation opportunities available by extending the term of temporary permits and creating a program for sharing unused guide days between permit holders.
Reduce barriers to accessing public lands for school districts, city recreation departments, and university groups.
Increase permit system transparency by directing the land management agencies to notify the public when new recreation permits are available and ensuring that agencies respond to permit requests in a timely manner.
Reduce permit fees and costs for small businesses and organizations
Help control liability insurance costs for permit holders by allowing them to use liability release forms with clients.
Additional elements of the EXPLORE Act include improving access to parks and public lands for veterans and people with disabilities by building additional accessible trails; the BOLT Act, which will create more long-distance biking trails; and the codification of FICOR and the Outdoor Recreation Legacy Partnership, which funds local parks and green spaces, and provides direct access to funding for tribes for developing green spaces.
AAC Member Andy Cochrane
AAC Executive Director Ben Gabriel synthesized this win, saying: “It has been such a privilege to work with all the outdoor recreation organizations, and legislators from both chambers and parties, to see the EXPLORE Act through. This historic recreation package will broadly serve the public, protect recreation resources, and provide for our gateway communities.”
As you might imagine, the AAC is thrilled with what this all means for public lands and accessibility to climbing across the United States! This win would not be possible without the combined efforts of our incredible partners, especially Outdoor Alliance, Access Fund, AMGA, and The Mountaineers.
Fixed Anchor Policy:
The National Park Service announced on December 18th that they were discontinuing the development of their proposed fixed anchor guidance. The update said that, "Park leaders will continue to manage climbing activities in Wilderness on a park-by-park basis consistent with applicable law and policy, including the Wilderness Act." This announcement comes nearly a year after Park officials sought public comment on proposed regulations which suggested a new interpretation of installations as defined in the Wilderness Act. This new interpretation, which could have prohibited fixed anchors in Wilderness, was met with significant concern from climbers, climbing organizations, and other recreation enthusiasts, as well as search and rescue professionals, throughout the country.
The AAC thanks the NPS for sensing the need to reevaluate the proposed regulations and looks forward to collaborating with them in the future on fixed anchor guidance.
The AAC, Access Fund, Mountaineers, and many other organizations, worked tirelessly to educate lawmakers on the potential impacts of prohibiting fixed anchors, which resulted in 14 Senators reaching out to the Secretaries of the Department of Interior and Department of Agriculture, requesting an update on the proposed regulations as well as emphasizing their disapproval of the interpretation of the Wilderness Act.
AAC Executive Director, Ben Gabriel, reflects: “We are thankful for the continued integrity and hard work of the NPS. Recognizing the balance of promoting recreation with the preservation of our natural resources, we look forward to working with NPS to develop sound policies that achieve both of these objectives.”
It is important to note that the United States Forest Service is continuing to consider their own proposed climbing management plan regarding fixed anchors in Wilderness areas, but their forthcoming decisions will be impacted by the PARC Act being signed into law.
Thank you to our many partners for their part in this work. Below, a few of these partners reflect on the significance of the discontinuation of the NPS proposal to their organizations and the climbers they represent:
“The Mountaineers commends the Department of the Interior for withdrawing its proposal to restrict fixed anchors in Wilderness areas. This decision protects sustainable climbing and safe outdoor education, and strengthens the conservation movement to protect public lands. We’re grateful that our federal leaders listened to the voices of climbers, outdoor educators, conservation advocates, Washington State’s U.S. Senators Cantwell and Murray, and all those who value the intersection between human-powered recreation and conservation.” –Tom Vogl, CEO, The Mountaineers
Time for a base camp nap. AAC Member Andy Cochrane
“As climbers, fixed anchors are essential pieces of our safety system that allow us to safely and sustainably access vertical terrain. Without fixed anchors, many of the wildest and most inspiring places in America would become inaccessible to the public.” —Heather Thorne, Executive Director, Access Fund
“This is a meaningful step in the ongoing dialog between the climbing community and the regulatory agencies, NPS and NFS. Protecting the Wilderness based on the fundamentals of clean climbing a la the Yosemite Climber's Credo is a needed collaboration with mutual goals. ‘United we stand!’”—Jerry Gallwas, YCA Board Chair
“I'm happy to see that wilderness climbing, in iconic locations and lesser-known crags, is protected thanks to the efforts of a broad coalition of passionate climbers and outdoor recreation allies. This decision ensures that climbers will continue to enjoy transformative experiences in these special areas while working toward balanced, long-term solutions that protect both wilderness and climbing access.”—Andrew Blann, Vice President, Arkansas Climber’s Coalition
The Prescription—Fall on Ice | Protection Pulled Out
Ice is a fickle medium that is hard to assess. This month we’re highlighting an accident report from ANAC 2023 involving a leader fall that was compounded by pulled protection. Though the climber was very experienced, this accident underlines that even as more people climb ice than ever before, it takes years of experience to accurately gauge conditions. Also, climate change is increasing the hazards of rockfall, avalanches, ice collapse, and generally warmer ice.
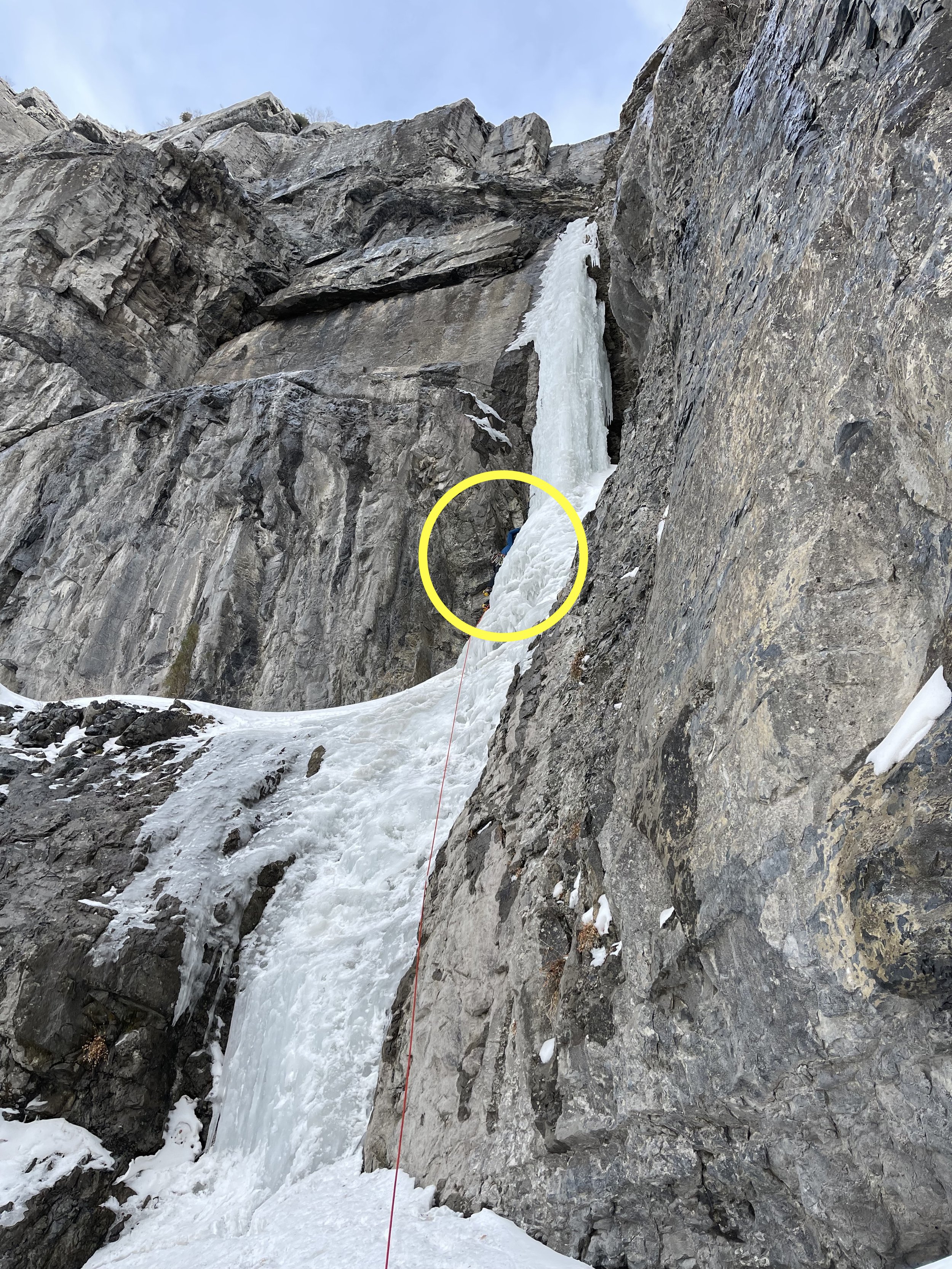
Tim Thompson (circled in yellow) climbing on the Finger of Fate prior to his accident. The gray, bubbly, and unbonded ice in the lower section of the photo reflects the warm temperatures on the day prior. Dustin Lyons
Fall on Ice | Protection Pulled Out
Provo Canyon, Upper Provo Falls
Utah County Sheriff’s Search and Rescue was dispatched at 11:09 a.m. on December 26 to aid an ice climber who had fallen from the first pitch of Finger of Fate (3 pitches, WI4+) in Provo Canyon.
The climber, Tim Thompson (29), was nearing the end of the first pitch when ice sheared from under his left foot. He wrote to ANAC that he was “pushed forward into my ice tools and my relaxed grip caused me to fall.” Thompson’s uppermost screw pulled out of the ice, causing him to fall a total of 50 feet.
Utah County team members arrived and, with the help of the climbers already on scene, evaluated the ice conditions, established an equalized anchor with six screws at the base of the climb, and developed a plan to move the patient horizontally about 100 feet over steep, slippery terrain to a five-by-ten-foot ledge that was out of the rockfall and icefall area. Conditions were deteriorating, the ice was becoming less cohesive as temperatures rose, and rocks were starting to fall.
A Department of Public Safety (DPS) helicopter crew did a reconnaissance of the ledge and determined that it would be a suitable place for a hoist operation. The patient was then short-hauled from the ledge to a nearby parking lot, where an ambulance was waiting. He was airlifted to a hospital and assessed to have two broken vertebrae, a broken elbow, torn ligaments in an elbow, and a badly broken left wrist.
Tim Thompson after falling from the first pitch of Finger of Fate. Rescuers short-hauled him by helicopter to a waiting ambulance. Photo: Dustin Lyons.
ANALYSIS
Warm conditions make ice climbing hazardous. Recalls Thompson: “The weather was warm the day before. Temps overnight were about 28°F for almost 10 or 12 hours and were hovering around 31°F or 32°F while climbing. We felt confident that the ice had had enough time to heal, and that as long as we climbed quickly, we were in no danger.”
Running water, heat retained by the underlying rock, and even indirect solar radiation can prevent ice from refreezing. The warm temperatures also affected the quality of Thompson’s protection. He wrote to ANAC, “When I put in the last ice screw, the ice was really soft. Up until the last quarter of the route, the ice [had been] really healthy and the screw placements were really good. I got several really solid screws lower on the route, and the second-to-last one (the one that caught me) was in really bomber ice.”
Thompson did well to place extra gear that he might have dismissed as unnecessary. Before the final section of the pitch, he says, “I remember pulling onto the ice after a ledge rest and deciding to step back down and place a high screw. I knew that would be a lot of protection, as the last screw was just below my feet. But if I had not placed this screw, I would have hit the deck from almost 100 feet up. Things could have been a lot worse.”
Sources: Salt Lake County Sheriff’s Search and Rescue and Tim Thompson.
The Prescription—Video Series
Warm conditions make ice climbing hazardous. Pete Takeda, editor of Accidents in North American Climbing, and IMGA/AMGA Guide Jason Antin are back to explain the hazards ice climbers face in warm conditions, such as protection pulling, poor tool placements, and shearing crampons.
Producers: Shane Johnson and Sierra McGivney; Videographer: Foster Denney; Editor: Sierra McGivney
Location: Silver Plume Falls, Silver Plume, CO
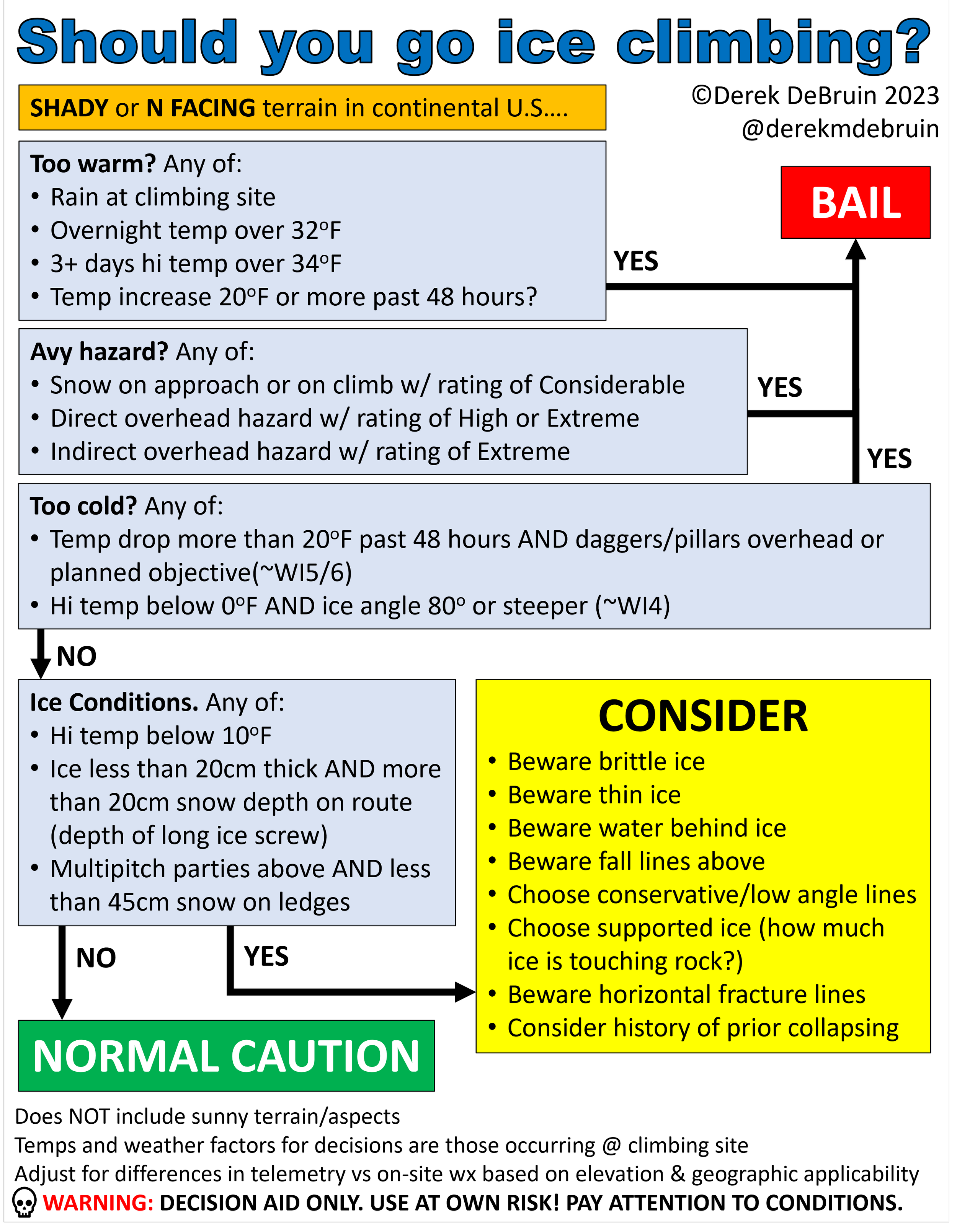
A NOTE FROM THE EDITOR
Over time an ice climber learns to gauge conditions and most importantly, when to go for it and when to back off. This is a long and experience-based learning curve. The biggest lesson is: If it doesn’t feel right, don’t do it. Whether a novice or an experienced ice climber, don’t factor luck into your decision-making.
Utah guide Derek DeBruin’s flowchart is a handy tool to assess ice climbing decision-making on any given day:
This flowchart can assist in managing hazards by helping determine the stability of the ice, the effectiveness of ice screw protection, and the quality of ice tool placements. Downloadable versions are available here.
Presented By:
Support This Work— Join or Give Today
Your contribution will significantly impact climbers—whether they are learning how to avoid accidents through our updated database, using research funding to analyze melting ice caps and the changing heights of iconic mountains, or pursuing first ascents around the world. Your gift makes these things possible.
Subscribe to AAC Emails
Guidebook XII—Member Spotlight
Josh Pollock “smedging” his way up Con Cuidado y Comunidad (5.6) at the Narrow Gauge Slabs. Land of the Ute and Cheyenne peoples. AAC Graphic Designer Foster Denney
Con Cuidado Y Communidad
By Sierra McGivney
Driving towards Highway 285, we pass strips of red rock cutting through the foothills of Morrison in Colorado’s Front Range, chasing the promise of new climbs. In the front seat, Josh Pollock describes the Narrow Gauge Slab, a new crag he has been developing in Jefferson County.
Pollock is the type of person who points out the ecology of the world around him. As the car weaves along the mid-elevation Ponderosa Pine forest, Pollock describes how we’ll see cute pin cushion cacti, black-chinned or broad-tailed hummingbirds, and Douglas-fir tussock moth caterpillars.
We pull into a three-level parking lot about seven miles down the Pine Valley Ranch Road. With no cell service and heavy packs, we set off along an old railroad trail toward the crag. Not even ten minutes into our walk, Pollock turns off, and we are greeted by a Jeffco trail crew building switchbacks to the crag.
As we approach the base of the Narrow Gauge Slab, Pollock picks up the dry soil. Fine granular rocks sit in the palm of his hand as he describes how this is the soil’s natural state because of Colorado’s alpine desert climate.
Photo by Anne Ludolph.
Unsurprisingly, Pollock was a high school teacher at the Rocky Mountain School of Expeditionary Learning in a past life; now, he is a freelance tutor and executive function coach. A Golden local and climbing developer, he has been working to develop the Narrow Gauge Slab since 2021.
Pollock first became interested in route development in 2011. He wasn’t climbing much then, instead focusing on raising his second child. Flipping through a climbing magazine one day, an article about route development caught his eye.
Between naps, diaper changes, and bottle-feeding cycles, he would go for quick trail runs in the foothills by his house in Golden. During his runs, Pollock noticed cliffs that weren’t in guidebooks or on Mountain Project. He began imagining how future climbers might experience and enjoy the rock.
“The routes I can produce for the community are moderate and adventurous but accessible,” said Pollock.
Climbing in Clear Creek is a high-volume affair. Jeffco Open Space (JCOS), the land management department for Jefferson Country, started to recognize this during the five years from 2008 to 2013 when climbing in the area exploded. With such a high volume of all kinds of outdoor enthusiasts recreating in Jefferson County, including climbers, adverse impacts on the land followed, including increased erosion and propagation of noxious weeds. Previously, Jeffco Open Space took a more hands-off approach when it came to climbing. However, because their mission is to protect and preserve open space and parkland, they concluded the increased popularity of climbing in the area warranted more active management.
While Jeffco Open Space had a few climbers on staff, they quickly realized they were not qualified to make decisions surrounding fixed hardware and route development. They turned to the local climbing community.
In 2015, Pollock began developing routes at Tiers of Zion, a wooded crag overlooking Clear Creek Canyon in Golden. In 2016, Jeffco Open Space established the Fixed Hardware Review Committee (FHRC) with Pollock as one of its seven advisors—now eight. The FHRC provides expert analysis to Jeffco staff members regarding applications for installing or replacing fixed hardware in the area (including slacklining). As a formal collaborative effort between local climbers, route developers, and Jeffco land managers, it is one of the first of its kind in the country.
Eric Krause, the Visitor Relations Program Manager and Park Ranger with Jeffco Open Space, deals with literal and figurative fires weekly and is responsible for all climbing management guidelines. He sits in on meetings and speaks for Jeffco.
“I think really good communication between a landowner or land manager and the climbing community is imperative,” said Krause.
Since 2015, Jeffco Open Space has invested more than 1.5 million dollars to improve the access and sustainability of existing crags by stabilizing eroding base areas, building durable and designated access trails, supplying stainless steel hardware to replace aging bolts, supplying portable toilet bags to reduce human waste at crags, and rehabilitating unsustainable areas.
If new routes for an existing crag are submitted to the FHRC via their online form, it’s already an impacted area, so it’s more likely to be approved. During their quarterly meeting, each member of the FHRC reviews the submission and discusses whether the new route(s) is a worthwhile addition to climbing in Jefferson County. A route that might be denied is within the 5.7-5.10 range at a crag with limited parking and heavy trail erosion, because routes in that range tend to attract the highest volume of climbers.
“We don’t really want to be adding more sites that are just going to degrade, and we’d rather get in there ahead of time and build it out to where it’s sustainable to begin with,” said Krause.
If a new crag is submitted, this triggers an entirely different internal review process called the “New Crag Evaluation Criteria (NCEC),” overseen by Jeffco Open Space. Every individual on the JCOS internal climb- ing committee (comprised of staff from the Park Ranger, Trails, Natural Resources, Planning, Park Services, and Visitor Relations teams) independently rates the new crag based on various categories: potential access trails, environmental considerations, parking, traffic, community input, organizational capacity, visitor experience, and sanitation management. They then average all of the scores for the submitted crag, and its viability is discussed.
To combat the ever-growing need for accessible places for new climbers, families, guided parties, and folks looking for high-quality moderate climbing, Jeffco asked the FHRC and others if they could find a beginner-friendly new crag in the southern part of the county, where there are fewer climbing areas.
According to Krause, Pollock took this request to heart and started looking all over the county for a new crag. He struggled to find a place with adequate parking, access to bathrooms, and the ability to build new trails on stable ground. “Threading that needle is hard, and it took several years and maybe half a dozen possible locations to find one that worked,” said Pollock.
An open space staffer suggested he look at the area that is now the Narrow Gauge Slab.
When Pollock first walked along the base of what would become a major project in his life, the Narrow Gauge Slab, he felt compelled by the rock’s position, composure, and aesthetic. He began imagining routes to climb. The crack features broke the wall up into clean-looking panels.
For Pollock, unlocking the potential of a crag is an unanswered question until the last moment.
“There’s a great drama to it,” said Pollock.
He proposed the crag in 2021. The Narrow Gauge Slab would become the first crag approved under the NCEC framework.
“I think what I’m most excited about is that this whole endeavor has been collaborative and cooperative with Jeffco Open Space from the get-go,” said Pollock.
Jeffco is constantly playing catch up with erosion damage in an arid climate like the Front Range. At the Narrow Gauge Slab, Jeffco had the opportunity to identify and implement adequate infrastructure for the area before route development began.
“In some ways [it is a] first of its kind experiment, with building a sustainable access trail and stabilizing belay pads on the base area and things like that before lots of user traffic shows up,” said Pollock. The Boulder Climbing Community, the AAC Denver Chapter, and Jeffco collaborated to stabilize and build out the area before the crag opened to the public.
According to Pollock, the crag does not have a theme. Since this crag has many developers, and sometimes multiple developers to any given climb, the route names have personal meaning to the developers or the circumstances of the route. But when you look closely, a kaleidoscope of meaning comes into view: collaboration.
His primary objective with the Narrow Gauge Slab was to develop a moderate and accessible crag, but the project evolved into something much more: mentoring climbers on route development. He reached out to different LCOs, such as Cruxing in Color, Brown Girls Climb Colorado, Escala, Latino Outdoors, and the AAC Denver Chapter, inviting members to participate in a mentorship program based on route development. In total, there are 16 mentees and five mentors, plus Pollock. Despite uncovering the crag, Pollock has barely put any hardware in.
Route development is a niche aspect of climbing that requires extensive resources and knowledge. Pollock wanted to invite new groups of climbers who might not consider themselves route developers but were interested in learning. He is pleased that the mentees have learned from this project and are developing new routes near the Front Range. Some mentees have been swallowed whole by the development bug. Lily Toyokura Hill is so enthused that she was recently appointed to the nearby Staunton Fixed Hardware Review Committee.
Photo by Anne Ludolph.
Hill and Ali Arfeen collaborated on Bonsai, a 5.7 climb featuring a tiny tree sticking out of the rock. Hill, who is shorter, and Arfeen, who is taller, would take Pollock’s kid’s sidewalk chalk and mark key holds they could reach, helping to determine where they would place bolts when they were developing the route’s first pitch.
To the left is Con Cuidado y Comunidad (With Care and Community), a three-pitch 5.6 put up by (P1) Sharon Yun and AAC employee Xavier Bravo, and (P2+3) Maureen Fitzpatrick and Cara Hubbell.
While Pollock racks up to lead Con Cuidado y Comunidad, Douglas-fir caterpillars inter- rupt our conversation. Pollock stops, pointing out the fuzzy horned creature on his bag. He describes how their population erupts every seven to ten years. His father was a biology teacher, and both of his children are fascinated by ecology.
On top of Con Cuidado y Comunidad, we picnic overlooking the epic landscape of the South Platte. Pollock explains how climbing at the Narrow Gauge Slab requires what he calls “smedging,” a mix of smearing and edging.
Climbs are littered with minuscule footholds and often require both smearing and edging to climb. Pollock prefers this type of movement: slow and thoughtful.
The last bolt for the Narrow Gauge Slab was drilled on August 19, just in time for opening day on the 24th. Pollock feels immense pride in the crag.
“It is really satisfying to share the crag with folks and give to the community,” said Pollock.
On these south-facing slabs, there are thirteen routes ranging from 5.4 to 5.9+, spread across the crag’s granite rock. You can listen to the babble of the South Platte River as you climb, breathing in the smell of fresh pine needles as you stand up on a tiny food hold. Don’t forget to look out for the Douglas-fir caterpillars inching their way across the rock as you clip the bolts.
Support This Work— Join or Give Today
Your contribution will significantly impact climbers—whether they are learning how to avoid accidents through our updated database, using research funding to analyze melting ice caps and the changing heights of iconic mountains, or pursuing first ascents around the world. Your gift makes these things possible.
Guidebook XII—Grant Spotlight
The Emperor Face of Mt. Robson in water color and ink. AAC member Craig Muderlak
Mountain Sense
By Sierra McGivney
Usually, when Balin Miller encounters spindrift ice climbing, he puts his head down, waits for 10 to 20 seconds, and continues climbing. Halfway up the face of the Andromeda Strain, a line on the northeast face of Mount Andromeda in Alberta, Canada, Miller and his climbing partner Adrien Costa encountered an intense spindrift funnel. Thirty seconds passed, then one minute, two. After five minutes, he thought, f*** this, and downclimbed.
Miller was persistent, but the spindrift was relentless. They wasted a couple of hours trying to go around.
“You couldn’t see anything, even if you wanted to push through,” said Miller.
Miller and Costa peered around to where the climbing turned into a chimney. A wall of white snow poured down it. They turned back a pitch before the Hockey Stick Crack, disappointed that they wouldn’t be able to live the lore embedded in that pitch. This wouldn’t be the last time they tested their judgment in the mountains and turned away from an objective.
“I think what gets me most stoked for routes isn’t really how good they are, per se, but a lot of the history involved in it—the route that has some old trip report of people getting really scared on it,” said Miller.
This might be why Miller chose the Andromeda Strain as one of his objectives for this 2023 Mountaineering Fellowship Fund Grant (MFFG) trip. Apart from being one of the most popular yet serious alpine climbs in the Canadian Rockies, it has an epic story. An unsuccessful earlier group tried to ascend the off-width and found it too wide to take anything but one-foot lengths of hewn-off hockey sticks (an eerie, early rendition of the Trango Big Bro). Having no hockey sticks handy in 1983, Barry Blanchard, Dave Cheesmond, and Tim Friesen traversed beneath the off-width and around the corner to a steep snow-choked chimney that became the Hockey Stick Crack.
Miller originally applied for the MFFG from the American Alpine Club to support an expedition to the Alaska Range. He was awarded the grant but had to change his trip to the Canadian Rockies due to financial constraints. This grant funds climbers 25 years or younger seeking challenging climbs in remote places. One of Miller’s partners, Adrien Costa, has previously leveraged other AAC grants, including the Tincup Partner in Adventure Grant in 2021 and the Catalyst Grant in 2021 and 2023. The AAC grants can be a great jumping-off point for climbers looking to dream big.
Miller is an ice climber who spends his summers in Alaska and his winters in Bozeman. He got into climbing at the age of 12 and was versed in both ice and rock climbing growing up in Alaska. He is stalwart when it comes to ice climbing, but he has a goofy aura. You can deduce from photos of his trip that he doesn’t take himself too seriously, even on big alpine climbs.
After getting turned around on the Andromeda Strain, Miller and Costa climbed Dreambed (5.11 PG-13) on Mount Yamnuska and enjoyed a sunny day on rock. The two saw a weather window coming up and turned their gaze to Mount Robson or Yuh-hai- haskun (“The Mountain of the Spiral Road”), the highest peak in Canada. Infinite Patience (2200m, VI 5.9 WI5 M5) climbs the north side of the Emperor Face of Mount Robson until it merges with the Emperor Ridge (2500m, V 5.6). This was another big objective for Miller. Despite a solid weather window and the season being in their favor, new challenges awaited the group.
Aidan Whitelaw, six feet, four inches tall with a high-pitched voice, is one of Miller’s best friends. Despite being a student at Montana State University in Bozeman, he’s almost always down to skip class if it means going climbing.
With Whitelaw newly arrived, they set off on their adventure with only one rope, trying to go as light as possible. One rope between three climbers is OK if they don’t need to bail, but just in case, the team brought a Beal Escaper.
Miller wrote in his trip report: “Leaving the parking lot on October 5, Aidan Whitelaw, Adrien, and I hiked into Berg Lake, camping at the base of the face. [We] started up the face at 2 a.m. on the 6th. We soon realized that the direct start was out of condition. It’s usually [three pitches of WI 4 or 5] but turned out to be steep, wet melting snice. We opted to traverse right to gain Bubba’s Couloir. Unfortunately, there was no alpine ice left in the couloir. But the snow climbing was moderate but unprotectable. We eventually decided to bail after the House Traverse, which is roughly halfway up the Emperor Face to the ridge on Infinite Patience.”
Deciding to bail had become extremely obvious to the group. They encountered compact limestone with no cracks and nothing to sling. The group was fine leaving cams or pins but couldn’t find good placements to make anchors. They decided to deadman their ice tools, burying them to create a snow anchor to rappel off.
“It was the worst rock imaginable,” said Miller.
Eventually, they reached a bivy spot and got cozy, fitting three people into a two-person tent and Whitelaw and Miller into one sleeping bag. At noon the next day, they started their descent, which consisted of rappelling off V-threads and lousy rock anchors.
Balin Miller, Adrien Costa, and Aiden Whitelaw at the bivy spot on Infinite Patience getting cozy in a two-person tent. Land of the Mountain Metis, Stoney, Cree and Secwepemc peoples. AAC member Balin Miller
The Beal Escaper is a detachable rappelling device that allows you to descend on a single strand without permanently fixing the rappel and sacrificing the rope. To retrieve the rope, the climber tugs the rope ten to twenty times, causing the rope to inch through the Escaper and retrieve the rope.
The group was on 80-degree melting snow. No one had counted how many times they had pulled the rope to disengage the Escaper, but something was wrong. Everyone got quiet. They pulled as much rope through as they could, but ultimately, the rope refused to release. Unable to jug back up the rope out of fear that movement could release the device, and unable to solo back up because of 80 feet of steep bad snow and friable rock, they pulled out as much rope as they could and cut it. Only eight meters of rope were in their hands, the rest of it lost to the mountain. It was dark, and they didn’t know how far they were above the Mist Glacier.
They tied slings together as a pull cord, allowing them to do increments of full eight-meter rappels. Luckily, they were only 100 feet from the bottom.
Twenty-four hours later, Whitelaw was in class in Bozeman, Montana; no one was aware of the epic in the mountains he had just returned from.
Balin Miller questing off to lead a mixed pitch on Infinite Patience (VI5.9M5WI5).Land of the Mountain Metis, Stoney, Cree, and Secwepemc peoples. AAC member Adrian Costa
After several days off, Miller and Costa hiked into the Lloyd McKay Hut to attempt the north face of Alberta. However, they didn’t get the chance due to a storm and nine inches of wet snow. Miller wasn’t too bummed. Conditions weren’t in their favor, and there was always next year. Both Miller and Costa left after that, and Miller headed to Yosemite.
In November, Miller returned ready to ice climb. He climbed Suffer Machine (200m, WI5+ M7); Virtual Reality (100m, WI6+); Kittyhawk (150m, WI5), solo; and Nemesis (150m, WI6), solo.
He took a short break to visit his mom in Spokane, Washington. Ethan Berkeland flew out to meet him, and the pair drove about 430 miles back up to Canada with Slipstream in sight. Slipstream (900m, IV WI4+) climbs the east face of Snow Dome. It is infamous for it’s exposure to dangerous seracs, avalanches, and cornices, as evidenced by five reports in the Accidents in North American Climbing archive. Jim Elzinga and John Lauchlan first climbed it in 1979, and Mark Twight simul-soloed it in 1988 with Randy Rackliff.
“Anything Mark Twight does is awesome,” said Miller.
The previous fall, Miller had bailed after the approach when it had taken longer than expected, and “it just didn’t feel right.” Both Miller and Berkeland are solid ice climbers. They brought a full rope, a tagline, 14 screws, and a handful of draws, planning to solo the easier parts and pitch out the harder ones. They ended up simul-soloing the entire east face of Snow Dome on November 29 in four hours. In total, the day was thirteen hours from car to car.
After getting turned around on his previous alpine objectives, this was a great achievement for Miller.
Despite the epics on some of his original objectives, Miller found success. Each “failure” in the mountains is a lesson learned for the next climb, maybe even a cutting-edge ascent. The spindrift turned him around on Andromeda Strain, and Infinite Patience was out of condition, but Slipstream proved to be an amazing climb. Sometimes, infinite patience pays off in the mountains.
Support This Work— Join or Give Today
Your contribution will significantly impact climbers—whether they are learning how to avoid accidents through our updated database, using research funding to analyze melting ice caps and the changing heights of iconic mountains, or pursuing first ascents around the world. Your gift makes these things possible.
Guidebook XII—AAC Advocacy
Photos by Torch Pictures.
Teaming Up in DC
By The Editors
As the AAC’s General Counsel and Advocacy Director, Byron Harvison, put it, advocacy work is like “being in charge of building and maintaining an aircraft while it’s already flying in the air—and there are still no guarantees. This work requires constant attention to detail and management of hundreds of relationships.” To your average climber who cares about public lands and advocating for climbing landscapes, the constant awareness of legislative processes and advocacy relationships can be exhausting— the runout pitch where you’d rather cede the lead. But for the AAC advocacy team and our partners like Outdoor Alliance, it’s the money pitch—our opportunity to ensure the perspec- tives of our members and other recreationists inform the policies that shape America’s public lands and recreational spaces.
That’s why this September, the AAC advocacy team, including AAC President Nina Williams, AAC Executive Director Ben Gabriel, AAC Deputy Director Ashlee Milanich, and AAC General Counsel and Advocacy Director Byron Harvison, showed up in DC–to pay attention to the details. One of those key details is our partnership with Outdoor Alliance (OA), a coalition of outdoor recreation nonprofit organizations that work together towards our shared goals of conservation and protecting public lands. On just this one trip to DC, the AAC team joined up with our OA coalition members, holding more than 80 meetings over two days with members of Congress and the Administration to advocate for protecting public lands, improving outdoor recreation, and funding the outdoors. Plus, we hung out with Tommy Caldwell to swap stories and inform legislators about the power of climbing in these incredible landscapes.
The trip was a celebration of Outdoor Alliance’s 10th anniversary, and the many wins that a collaboration between outdoor recreationists can accomplish. Since Outdoor Alliance started ten years ago, the coalition has collectively helped protect 40 million acres of public land and water, secured $5.1 billion in funding for the outdoors, and been instrumental in empowering outdoor enthu- siasts to become outdoor advocates. New to the Outdoor Alliance is the Grasstops Collective. It is a leadership and advocacy development program that trains grasstops advocates to build relationships with policymakers and advocate for conservation priorities. Grasstops leaders are unique for their meaningful voice in their communities, whether they are in business, nonprofit, or local government. This trip featured the OA’s first cohort from the Grasstops Collective joining legisla- tive and agency meetings.
“The collaborative energy of all the Outdoor Alliance organizations representing different sectors of the outdoor community was amaz- ing! There is a definite impact on legislators and their staff members when we all come to the table together. I’m a climber sitting next to a surfer and a paddler and a biker, and we all have different but equally compelling stories to share on why this legislation (the EXPLORE Act) should pass,” reflected Harvison.
One of OA and the AAC’s biggest policy priorities for the end of the year is the EXPLORE Act. The recreation community has been working for years on proposals to strengthen, protect, and expand outdoor recreation opportunities on our public lands and waters. As participation in outdoor recreation grows, it becomes even more important that public land management agencies like the Forest Service, Park Service, and Bureau of Land Management have sound policies and resources in place that will support sustainable and equitable outdoor recreation access. The EXPLORE Act is a first-of-its-kind package of recreation policy. It includes provisions that would safeguard rock climbing, identify and create long-distance bike trails, improve recreational permitting for outfitters and guides, and make permanent the Outdoor Recreation Legacy Partnership, which provides grants for green space in urban areas. Notably, the much talked about PARC Act, heavily supported by the Access Fund, is bundled into the EXPLORE Act, with the intention to protect the responsible use of bolts in Wilderness areas.
“The Outdoor Alliance 10th anniversary cele- bration in Washington DC reinforced the collective energy and determination needed to advance legislation like the EXPLORE Act. It highlights how partnerships are essential to advocating in service of our members,” said Ben Gabriel when reflecting on the power of the week-long trip.
Congress has a lot on its plate, including determining a federal budget, wading through the complexity of major wars throughout the world, and much more. With all that to work through, it’s no wonder that the EXPLORE Act has continued to be deferred as a main concern. However, there is overwhelming bipartisan support in the House and the Senate for the EXPLORE Act, and several complex paths for it to potentially pass. It’s all in the details, which is where outdoor advocates and policy leaders can step in.
We were joined by champions from American Whitewater, Access Fund, American Canoe Association, IMBA, The Mountaineers, Surfrider, Winter Wildlands Alliance, and leaders from the OA Grasstops Collective, as well as by partners at REI and Patagonia.
Support This Work— Join or Give Today
Your contribution will significantly impact climbers—whether they are learning how to avoid accidents through our updated database, using research funding to analyze melting ice caps and the changing heights of iconic mountains, or pursuing first ascents around the world. Your gift makes these things possible.